Unit 7
IP Security
Unit Topics
- IP Security Overview
- IP Security Policy
- Encapsulating Security Payload
- Combining Security Associations
- Internet Key Exchange
- Cryptographic Suites
1. IP Security Overview
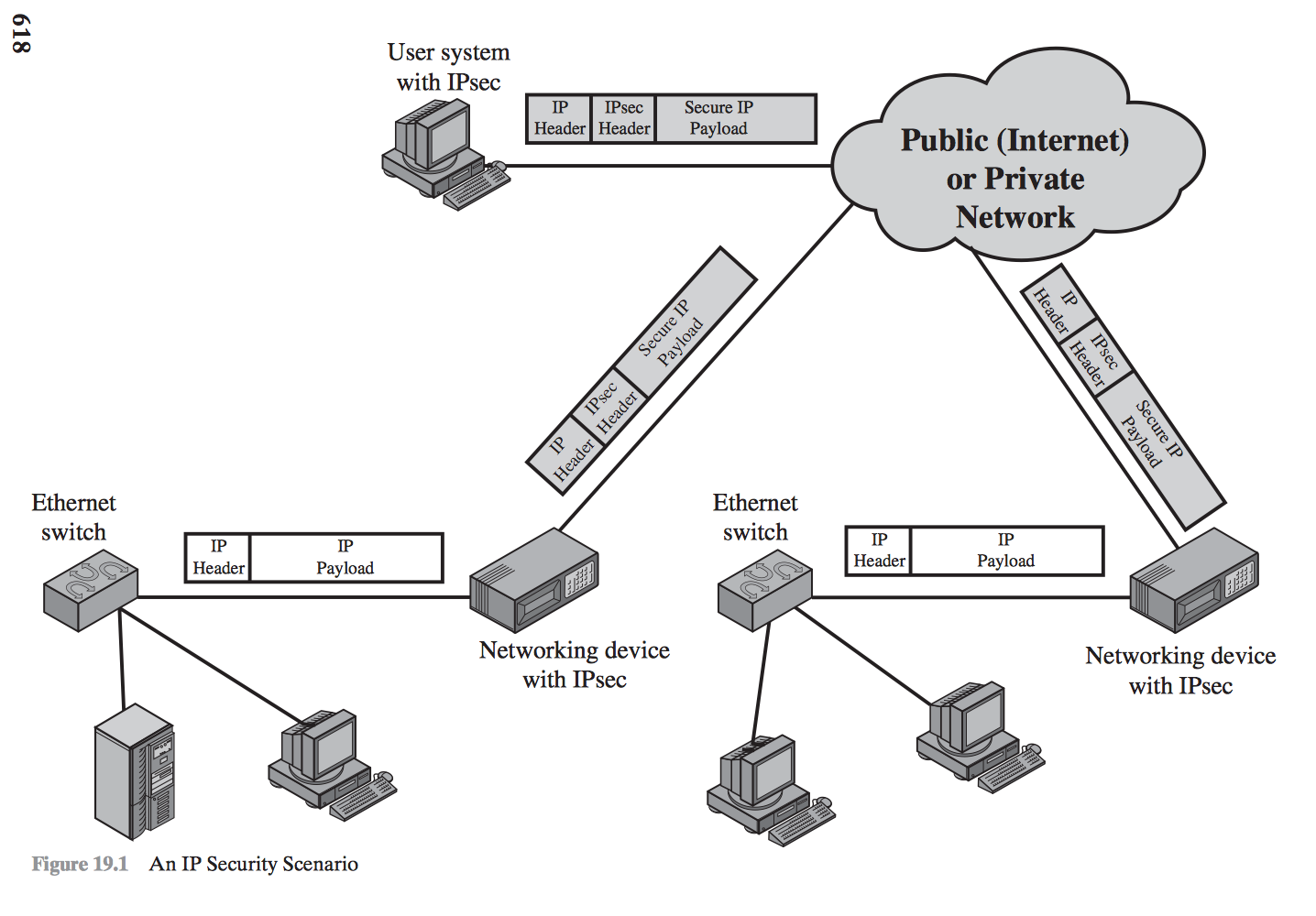
Application of IPsec
- Secure branch office connectivity over the Internet
- Secure remote access over the Internet
- Establishing extranet and intranet connectivity with partners
- Enhancing electronic commerce security
Benefits of IPsec
-
When IPsec is implemented in a firewall or router, it provides strong security that can be applied to all traffic crossing the perimeter.Traffic within a company or workgroup does not incur the overhead of security-related processing.
-
IPsec in a firewall is resistant to bypass if all traffic from the outside must use IP and the firewall is the only means of entrance from the Internet into the organization.
-
IPsec is below the transport layer (TCP, UDP) and so is transparent to applications. There is no need to change software on a user or server system when IPsec is implemented in the firewall or router. Even if IPsec is implemented in end systems, upper-layer software, including applications, is not affected.
-
IPsec can be transparent to end users.There is no need to train users on security mechanisms, issue keying material on a per-user basis, or revoke keying material when users leave the organization.
-
IPsec can provide security for individual users if needed.This is useful for offsite workers and for setting up a secure virtual subnetwork within an organization for sensitive applications.
Functional areas
- Authentication
- Confidentiality
- Key management
IPsec Services
- Access control
- Connectionless integrity
- Data origin authentication
- Rejection of replayed packets
- Confidentiality (encryption)
- Limited traffic flow confidentiality
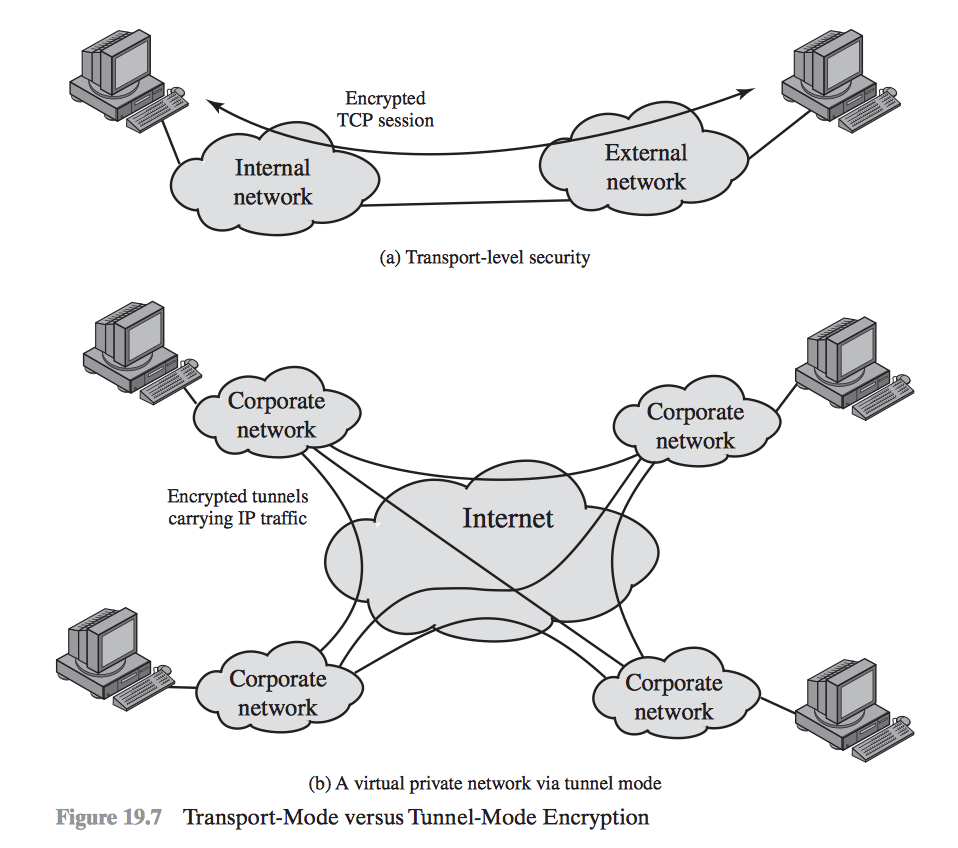
Modes of IPsec
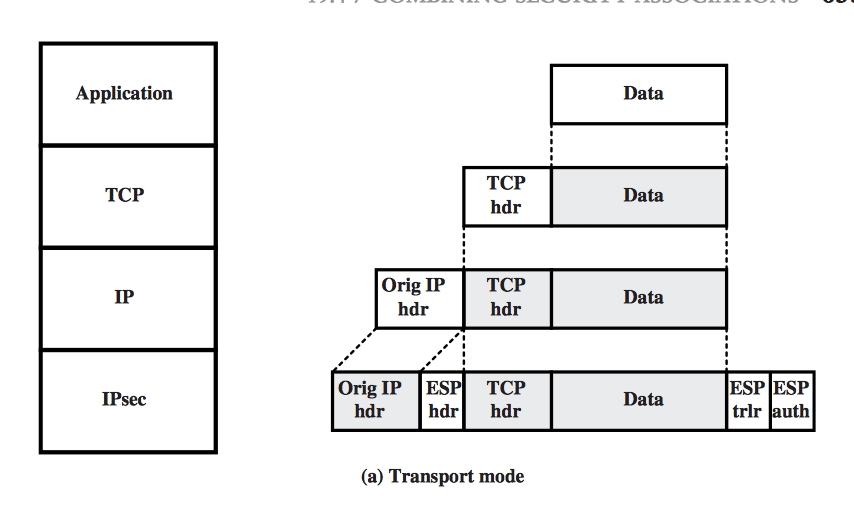
- Transport Mode
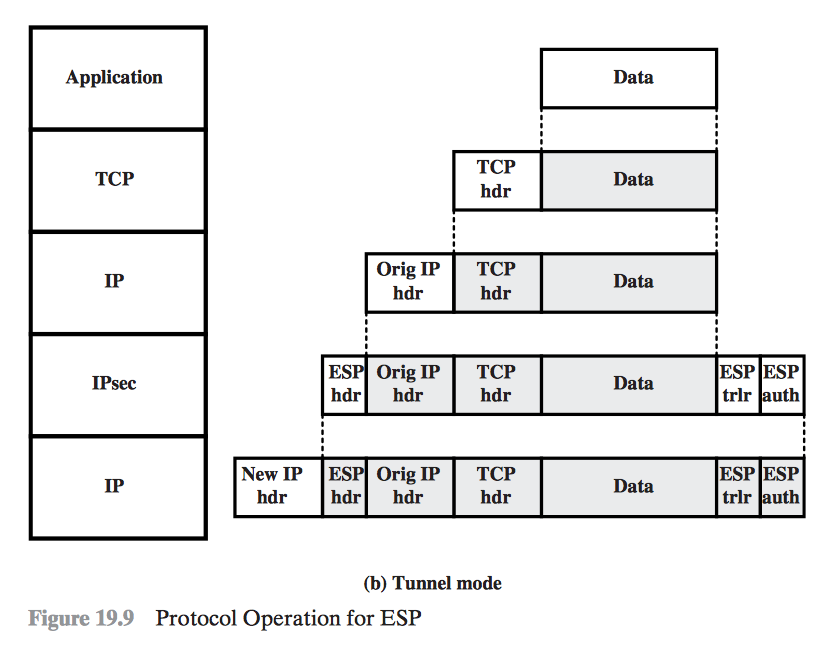
- Tunnel Mode