BSCIT
Network Security
Unit 5
Wireless Network Security
Unit 5
#[fit] Wireless Network Security
5 Topics
- IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Overview
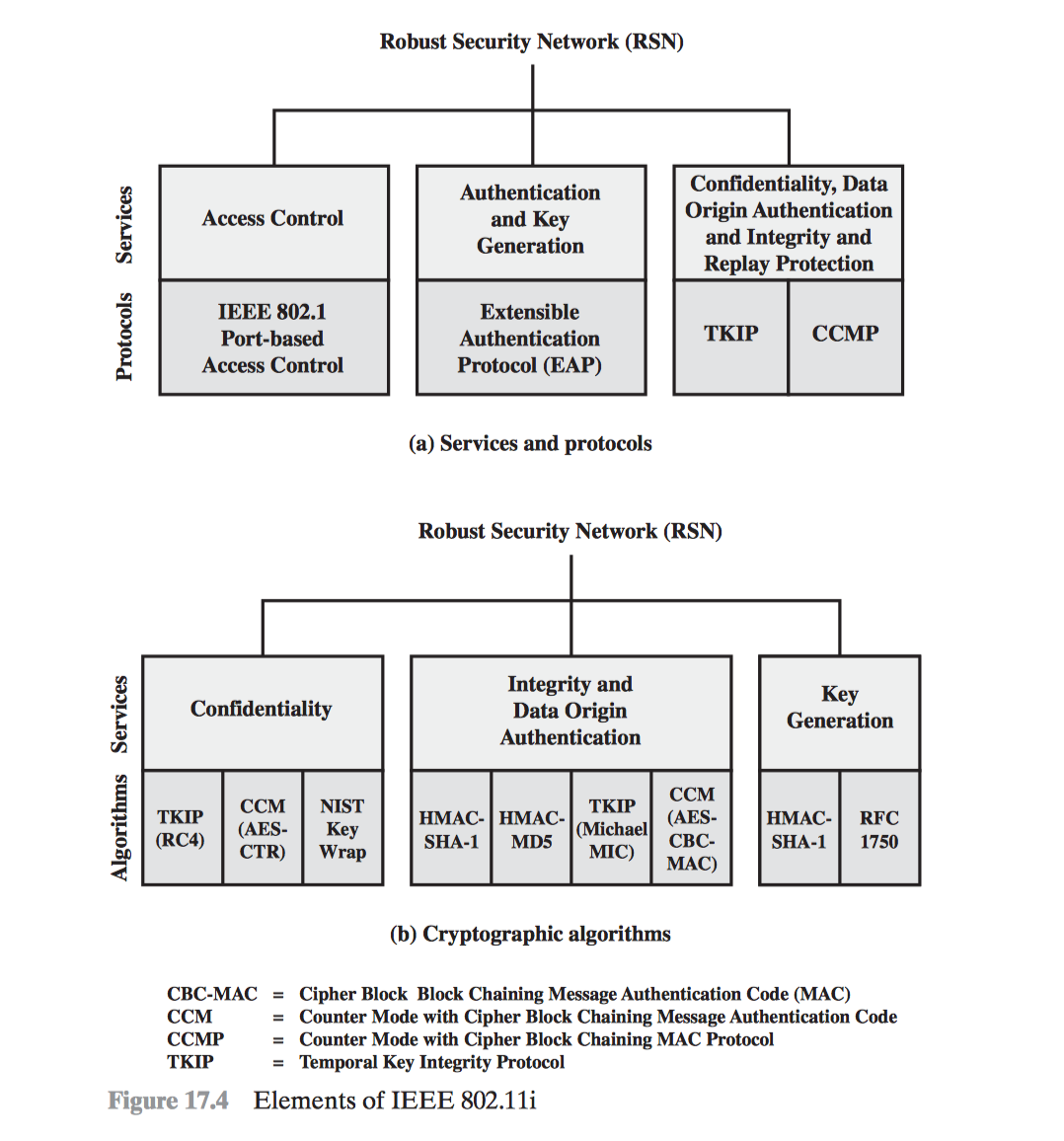
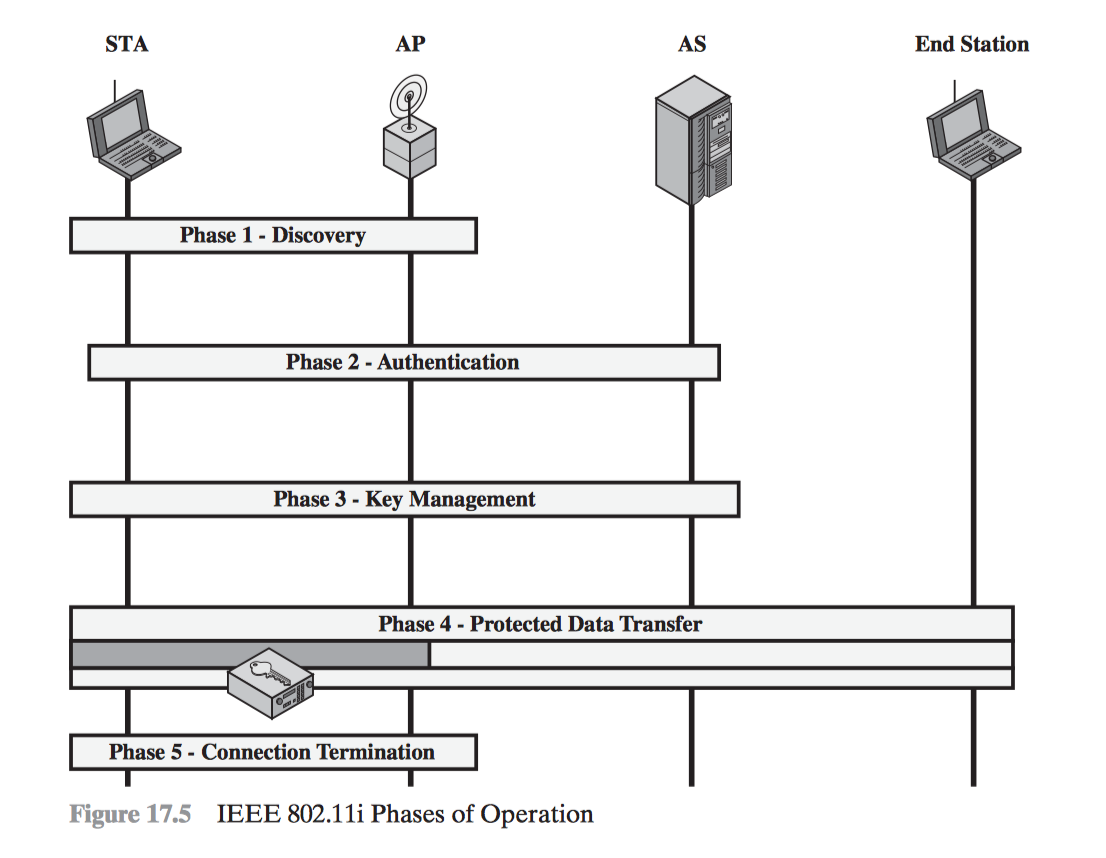
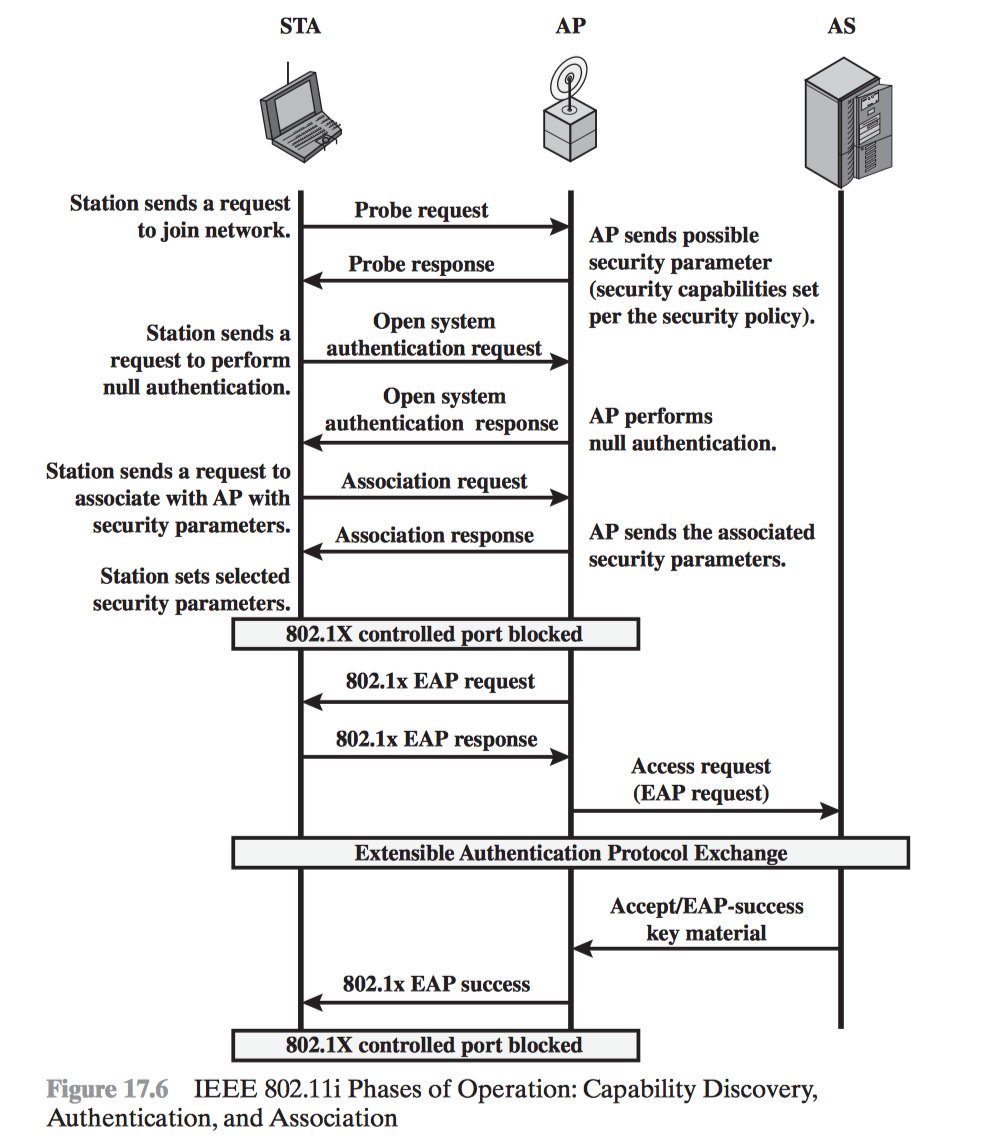
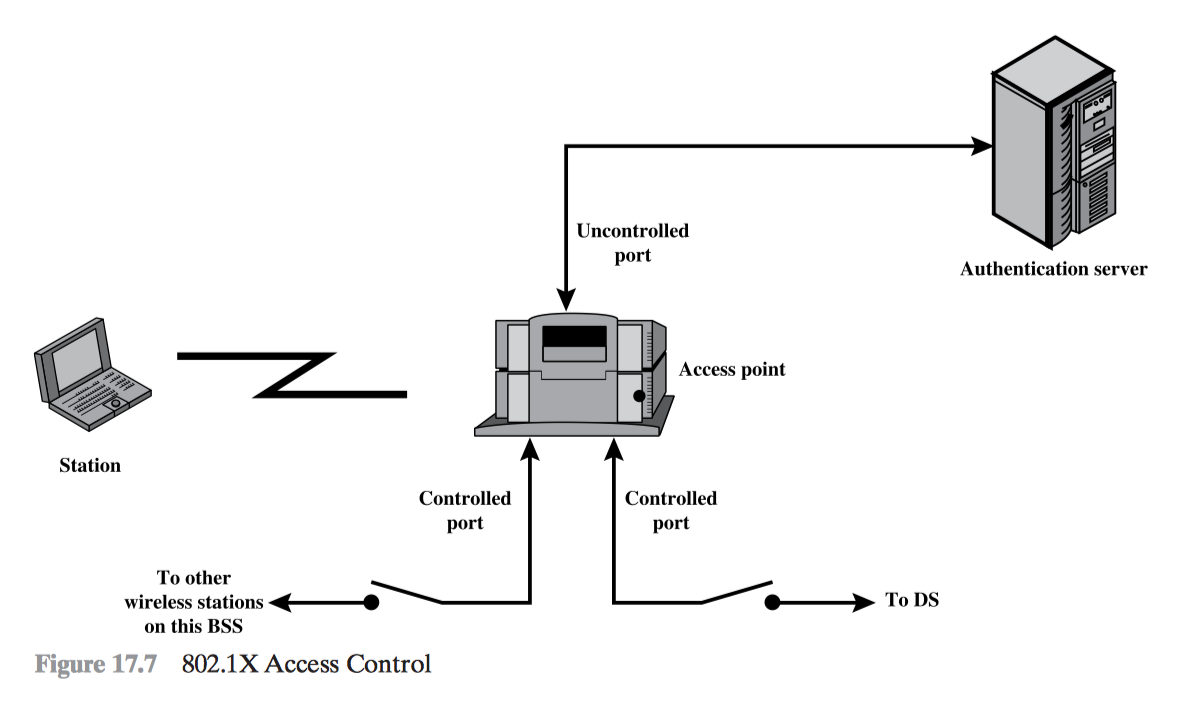
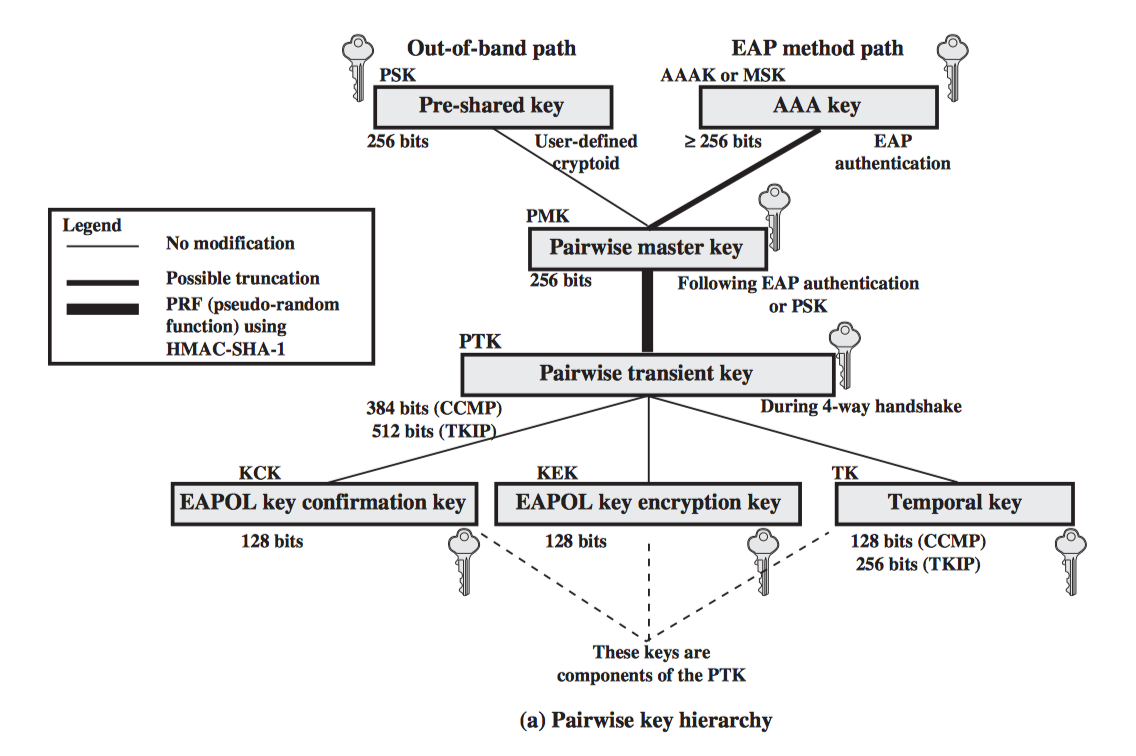
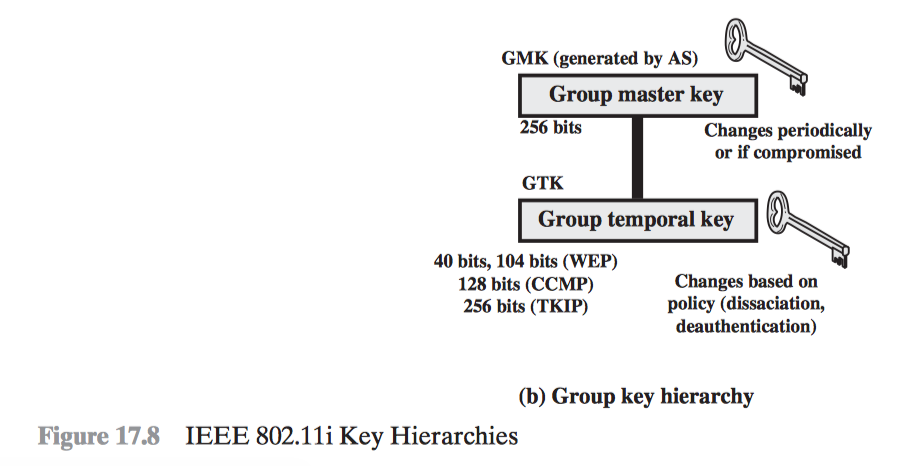
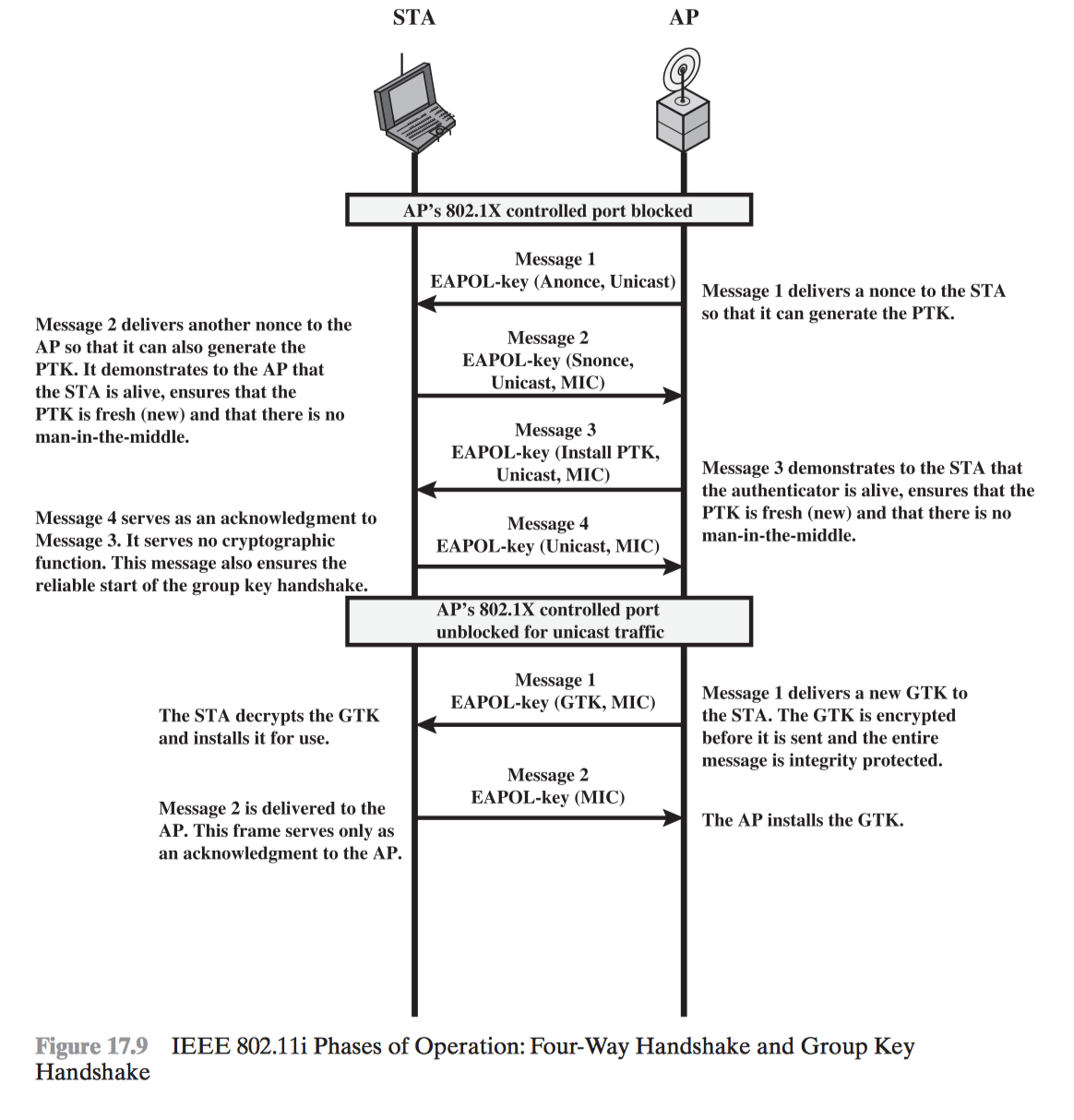
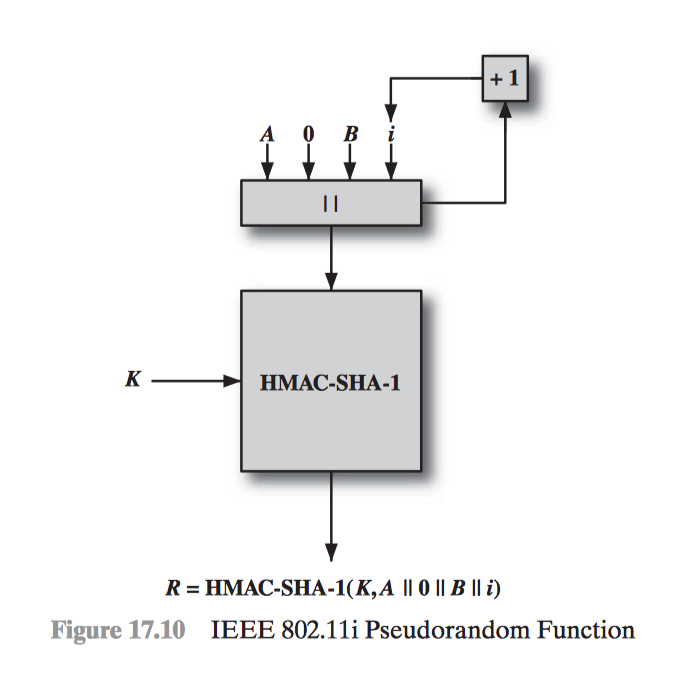
- IEEE 802.11i Wireless LAN Security
- Wireless Application Protocol Overview
- Wireless Transport Layer Security
- WAP End-to-End Security
1. IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Overview
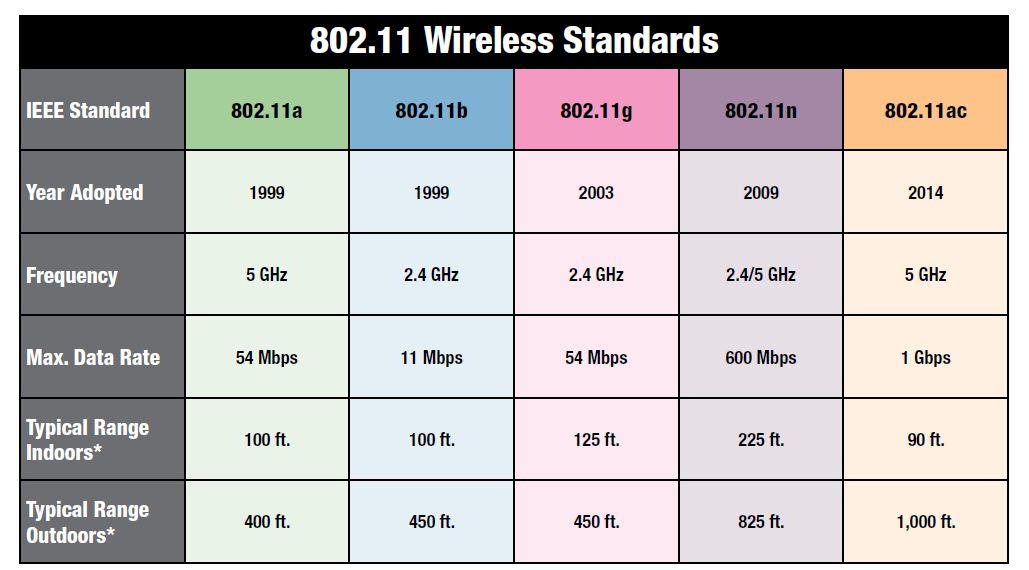
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Overview (4)
- The Wi-Fi Alliance
- IEEE 802 Protocol Architecture
- IEEE 802.11 Network Components and Architectural Model
- IEEE 802.11 Service
1. The Wi-Fi Alliance
- IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- IEEE 802 - Committee - LAN
- IEEE 802.11 - Committee - WLAN
- Develop a protocols and transmission specifications for WLANs
- WECA - Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance
- Industry Consortium
2. IEEE 802 Protocol Architecture
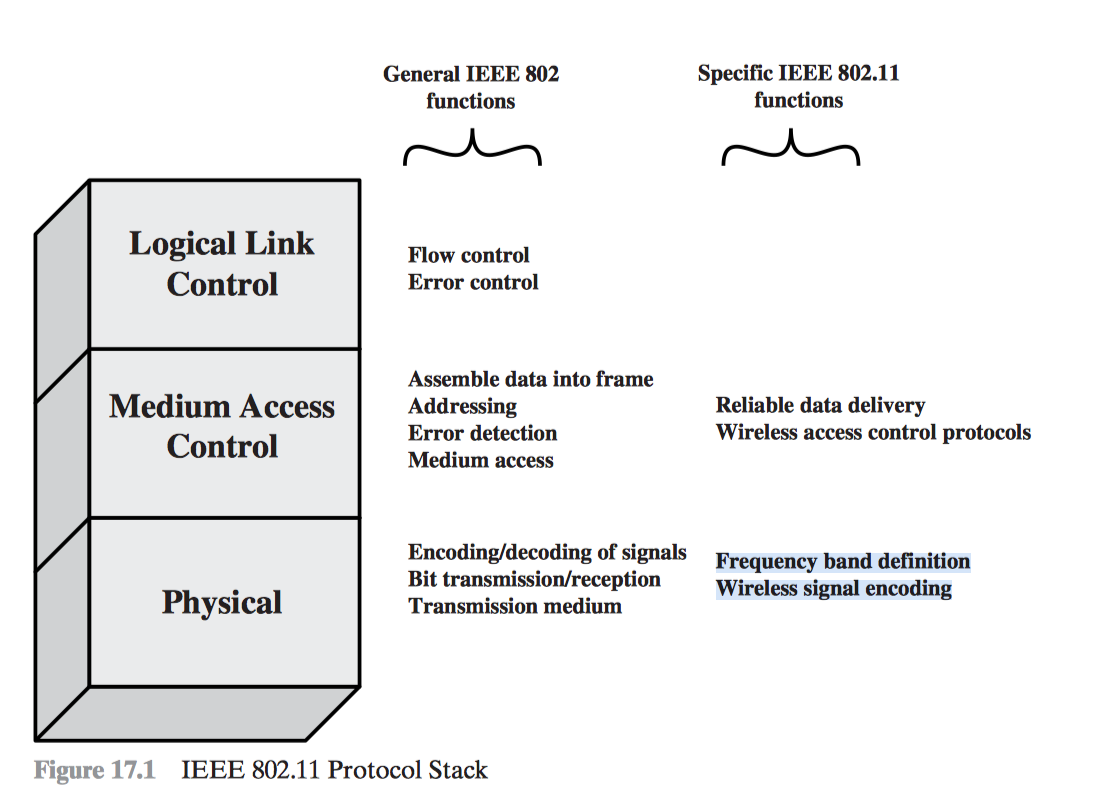
2. IEEE 802 Protocol Architecture
- Logical Link Control
- Media Access Control
- Physical Layer
1. Logical Link Control
- Flow Control
- Error Control
2. Media Access Control
- Assemble data into frame (MSDU -> MPDU)
- Addressing
- Error detection
- Medium access
- Specific IEEE 802.11 functions
- Reliable data delivery
- Wireless access control protocols
MPDU - MAC Protocol Data Unit MSDU - MAC Service Data Unit
3.Physical Layer
- General IEEE 802 functions
- Encoding/decoding of signals
- Bit transmission/reception
- Specification of Transmission medium
- Specific IEEE 802.11 functions
- Frequency band definition
- Wireless signal encoding
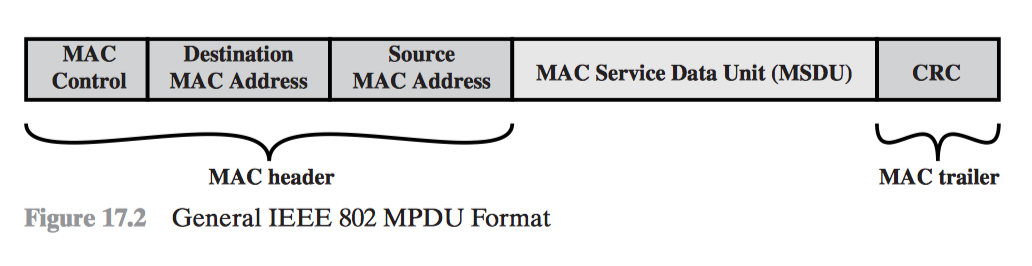
MPDU Frame Format
- Header
- MAC Control
- Dest. MAC Address
- Source MAC Address
- Body
- MSCU (Mac Service Data Unit)
- Trailer
- CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) /FCS(Frame Check Sequence) Field
MPDU Frame Format
3. IEEE 802.11 Network Components and Architectural Model
3. IEEE 802.11 Network Components and Architectural Model
- BSS - Basic Service Set
- DS - Distribution System
- AP - Access Point
- IBSS - Independent BSS
- ESS - Extended Service Set
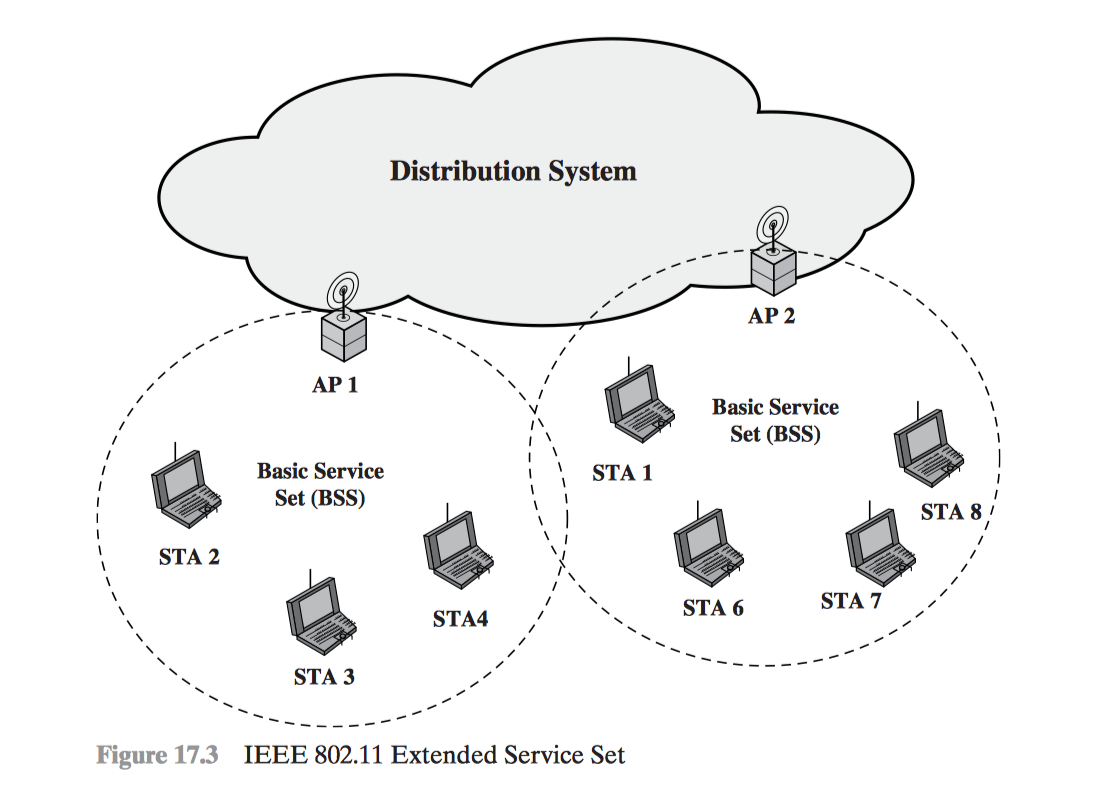
Basic service set (BSS) The smallest building block of a wireless LAN, which consists of wireless stations executing the same MAC protocol and competing for access to the same shared wireless medium.
A BSS may be isolated, or it may connect to a backbone Distribution system (DS) through an access point (AP).The AP functions as a bridge and a relay point.
When all the stations in the BSS are mobile stations that communicate directly with one another (not using an AP), the BSS is called an independent BSS (IBSS). An IBSS is typically an ad hoc network.
IEEE 802.11 Service
IEEE 802.11 Service
- Services that needs to be provided by the wireless LAN to achieve the functionality equivalent to that which is inherent to wired LAN.
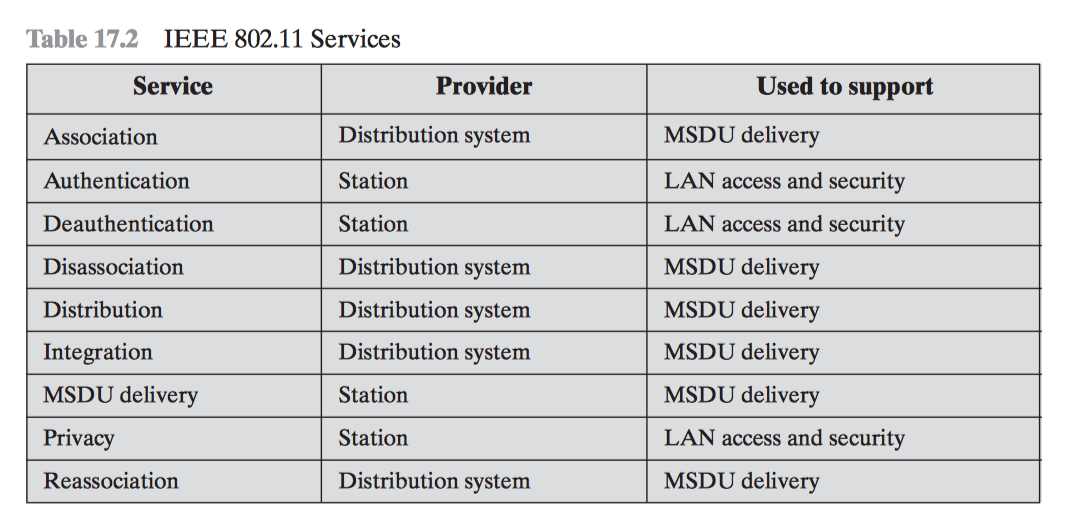
Categeorization of Service
- Based on Provider
- DS - Distribution System
- SS - Service Station
- Based on the Nature of Service
- LAN Access
- MSDU Delivery
- Distribution of Messages within a DS
- Association related services
- 3 Transition types
- No Transition
- BSS Transition
- ESS Transition
- 3 Services
- Association
- Reassociation
- Disassociation
- 3 Transition types
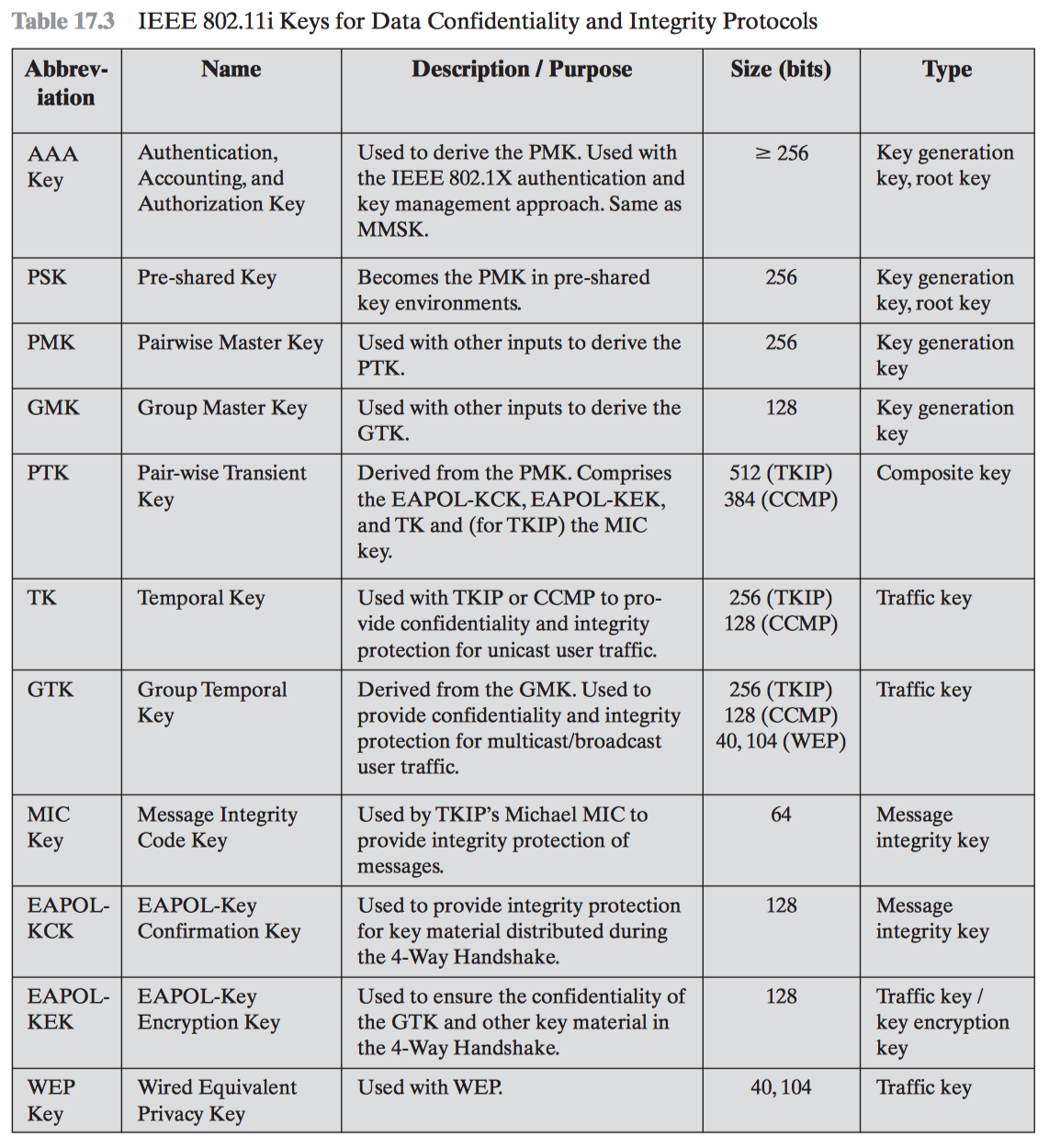
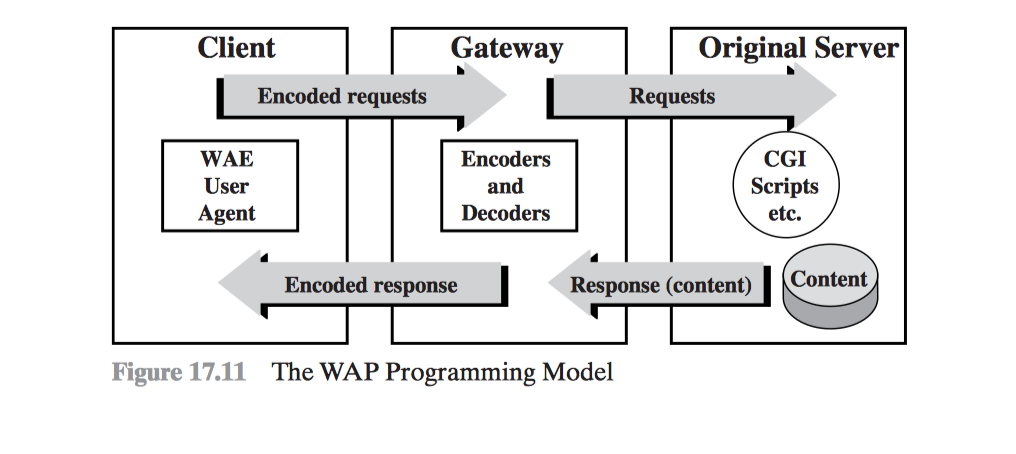
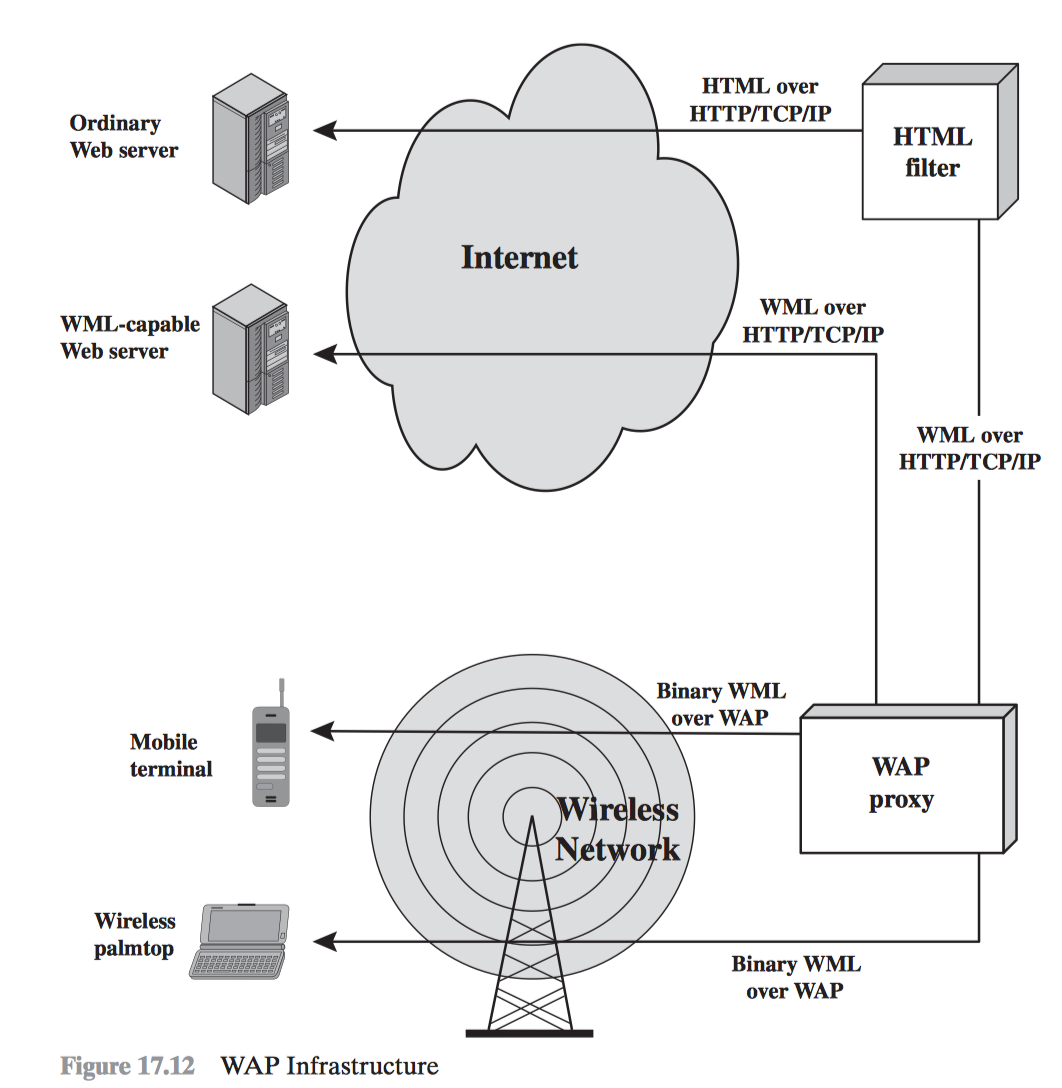
#[fit] WAP #[fit] Wireless Application Protocol
History
- Introduced in 1999
- Used widely in early 2000s
- By 2010 use of WAP Declined
WAP Key points
- WAP used WML (wireless markup language)
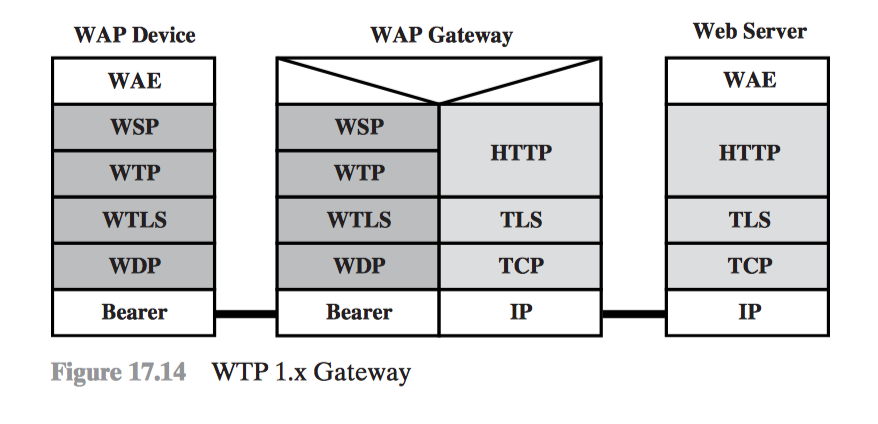
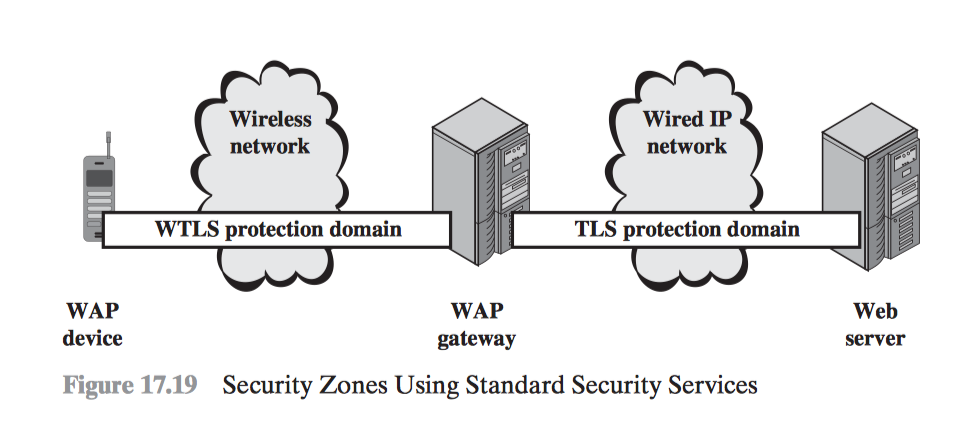
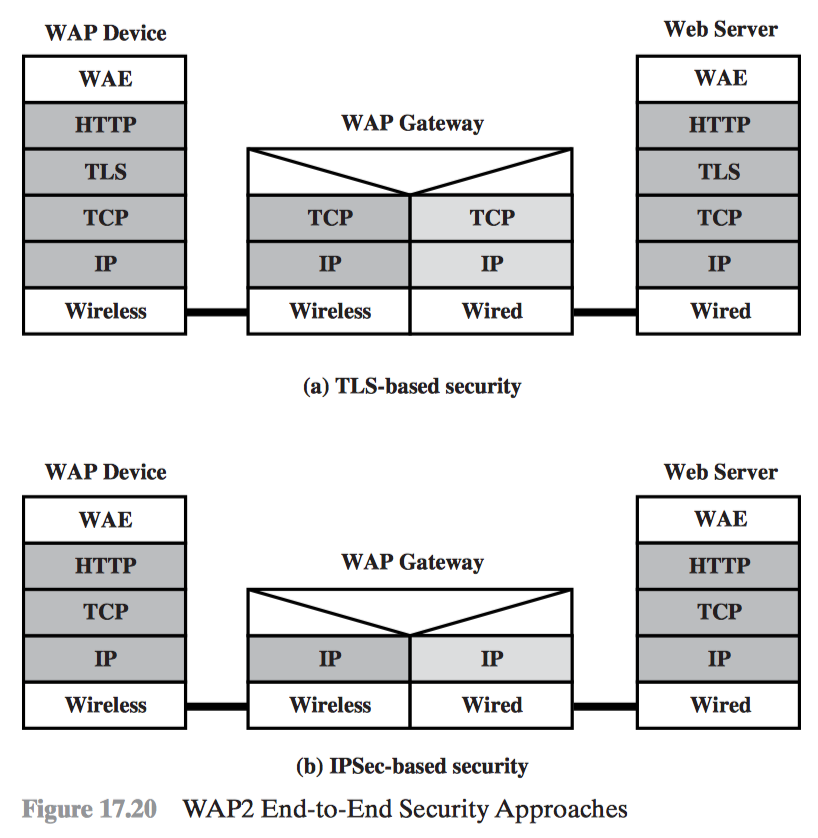
WAP Protocol Stack
Wireless Application Environment (WAE) Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP)