BSCIT
Network Security
Unit 4
Transport Level Security
Unit 4
#[fit] Transport Level Security
Topics
- Web Security Issues
- Secure Socket Layers (SSL)
- Transport Layer Security (TLS)
- HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocols)
- Secure Shell (SSH)
#[fit] 4.1 Web Security Issues
[fit] http:// ⚔️ https://
[fit] 4.1.1 Web Security Threats
[fit] 4.1.2 Web Traffic Security Approaches
4.1.1 Web Security Threats
Two way of grouping Web Security Threats
> Nature of attack.
> Location of Attack.
Nature of attack.
1 Active Attack
2 Passive Attack
Location of Attack.
Client Server Architecture

3 Locations for attack
- Client
- Server
- Network
In the context of web
- Web browser
- Web server
- Network traffic in between them
OSI Reference Model



SSL History
- SSL V1
- SSL V2
- SSL V3 / TLS V1.0
- TLS V1.1
- TLS V1.2 (Latest)
- TLS V1.3 (Draft)
SSL Concepts
- SSL Connection
- SSL Session
SSL Architecture
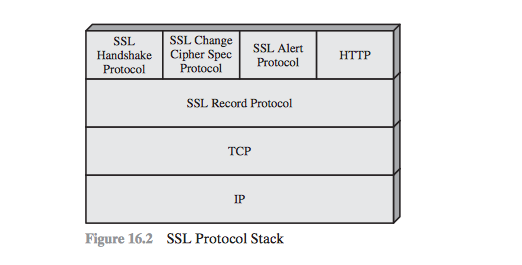
SSL Architecture
- SSL Record Protocol
- The Change Cipher Spec Protocol
- The Alert Protocol
- The Handshake Protocol
- The Change Cipher Spec Protocol
SSL Record Protocol
- Services
- Message Integrity using MAC
- Confidentiality using Symm. Enc.
- Operation (6 Steps)
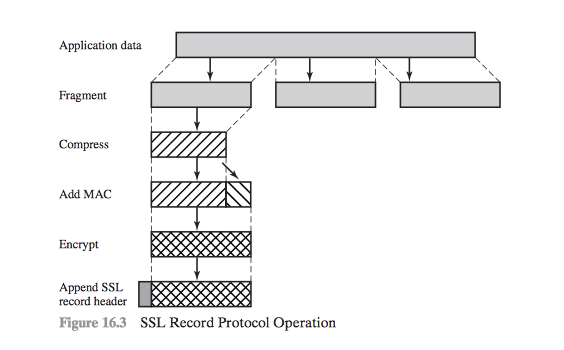
Operation (6 Steps)
- App Data from Application Layer
- Fragmentation
- Compass
- Add MAC
- Encrypt
- Add SSL Record Header
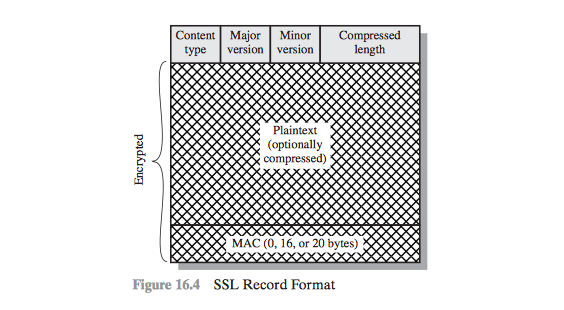
SSL Record Header
- Content Type (‘text/html’, ‘audio/mp3’, ‘image/png’)
- Major Version
- Minor Version
- Compressed Length
SSL Record Protocol
-
- The Change Cipher Spec Protocol
-
- The Alert Protocol
-
- The Handshake Protocol
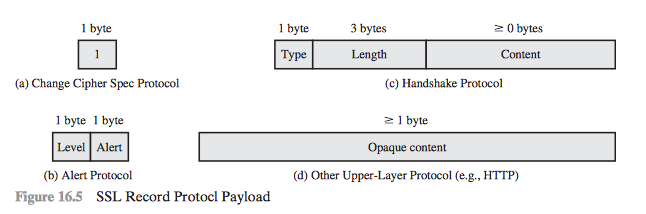
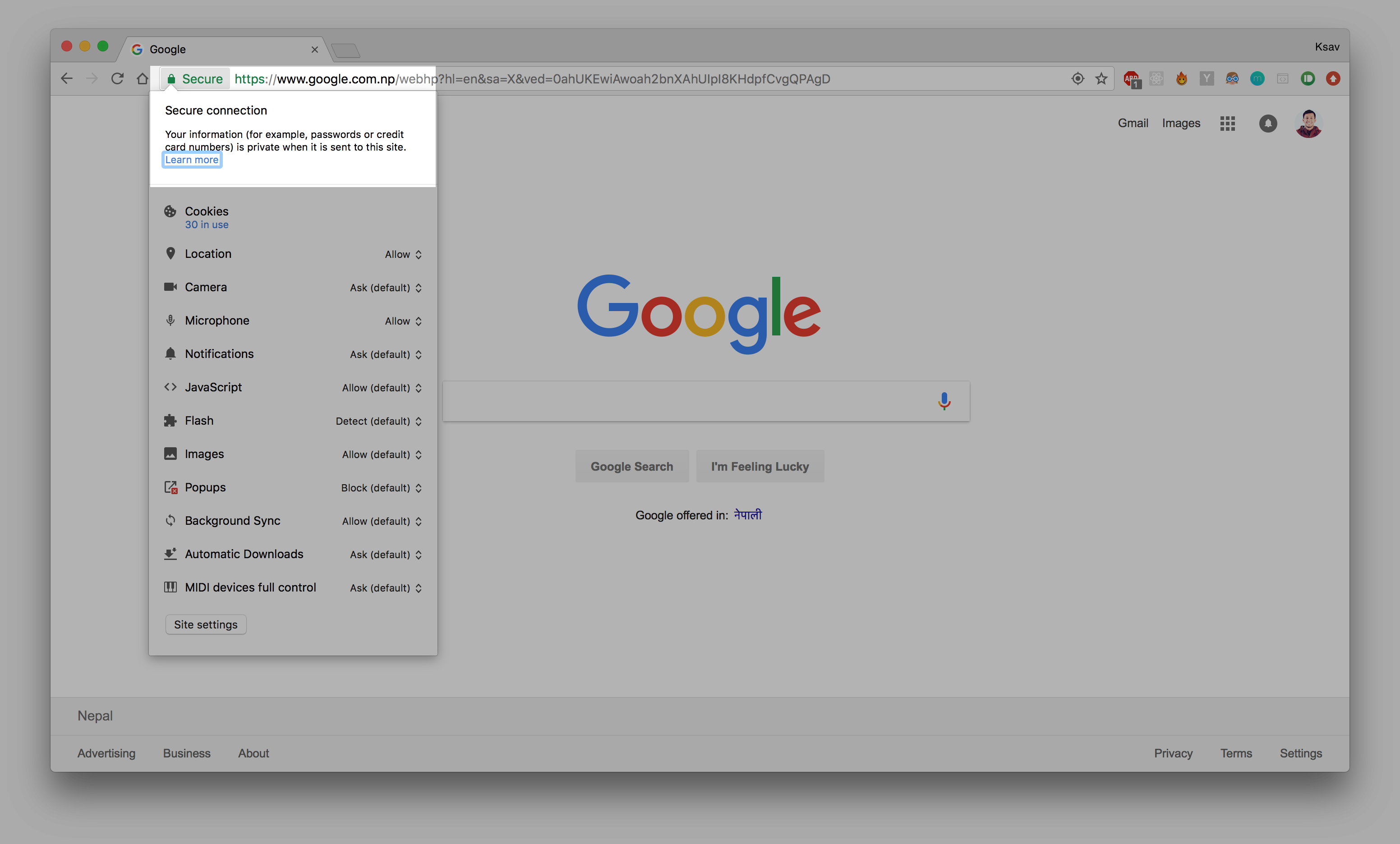
1. The Change Cipher Spec Protocol
- Simplest
- Consists of single message
- Single Byte with Value 1
- Causes the pending state to be copied into the current state, which updates the cipher suite to be used on this connection.

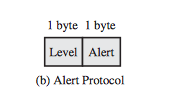
2. Alert Protocol
- Convey SSL alerts to the peer-entity
- 2 Bytes
- First Byte - Denotes level of the message
- Warning
- Fatal
- Alert code for specific alert
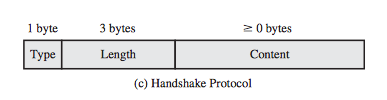
3. Handshake Protocol
- Size: Minimum 4 Bytes
- Type (1B) indicates one of 10 SSL Handshake Protocol Message Types
- Length (3B) indicates length of message in Bytes
- Content (>=0B) indicates the parameters associated with the messages
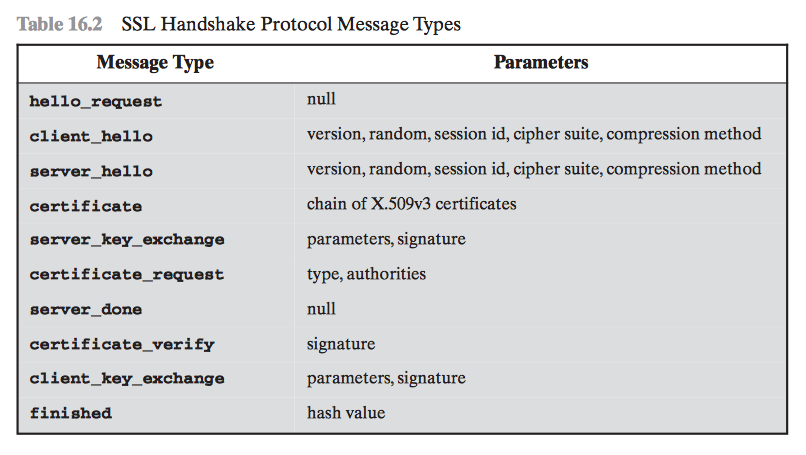
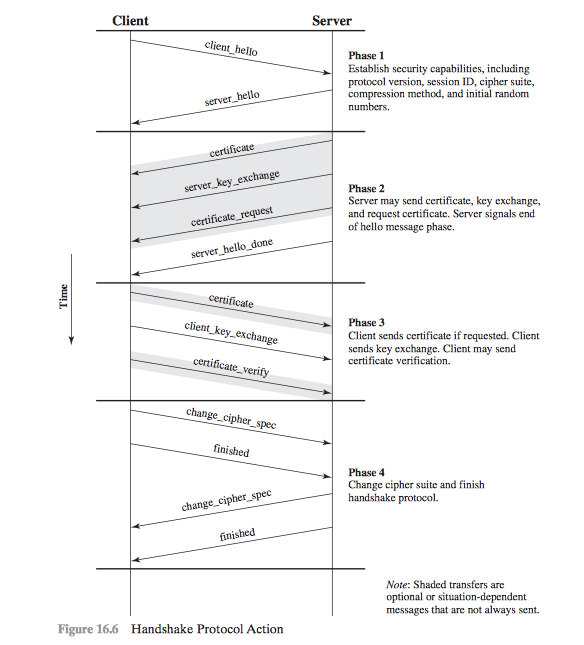
4 Phases of SSL Handshake
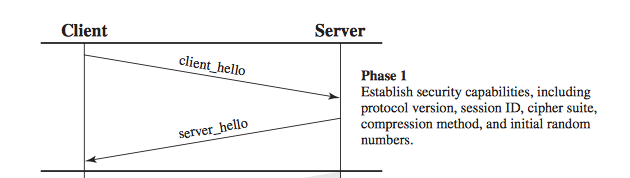
- Establish Security Capabilities
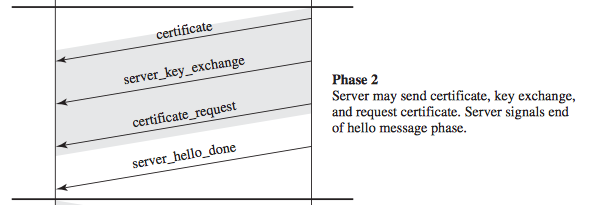
- Server Authentication and Key Exchange
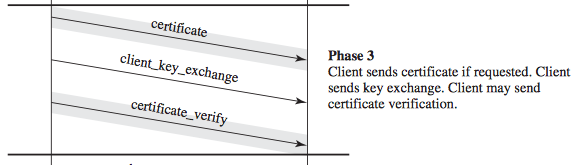
- Client Authentication and Key Exchange
- Finish