Unit 3
User Authentication Protocols
User Authentication Protocols
- Remote User Authentication Principles
- Remote User Authentication Using Symmetric Encryption
- Kerberos
- Remote User Authentication Using Asymmetric Encryption
- Federated Identity Management
Unit 3 - Key Points
Mutual authentication protocols enable communicating parties to satisfy themselves mutually about each other’s identity and to exchange session keys.
Kerberos is an authentication service designed for use in a distributed environment.
Kerberos provides a trusted third-party authentication service that enables clients and servers to establish authenticated communication.
Identity management is a centralized, automated approach to provide enterprise-wide access to resources by employees and other authorized individuals.
Identity federation is, in essence, an extension of identity management to multiple security domains.
3.1 Remote User Authentication Principles
- Mutual Authentication
- One-Way Authentication
3.1.1 Mutual Authenentication
Such protocols enable communicating parties to satisfy themselves mutually about each other’s identity and to exchange session keys.
2 Steps of User Authenentication
- Identification Step
- Verification Step
[fit]Four general means of authenticating a user’s identity
- Something the individual knows
- Password || PINS - Something the individual possesses
- TOKENs - Something the individual is
- Static biometrics - fingerprint || retina || face - Something the individual does
-
Dynamic biometrics - Voice Pattern Handwriting characteristics
#[fit] Challenges in Mutual Authentication
- Confidentiality
- Masquerade
- Compromization of Session Keys
- Prior existence of secret or public keys
- Timeliness
- Replays
4 Types of Replay Attacks
- Simple Replay
- Repetion that can be logged
- Repetition that cannot be detected
- Backward replay without modification
Mitigating Replay Attacks
- Sequence Numbers
- Timestamps
- Challenge / Response
3.1.2 One-Way Authenentication
3.2 Remote User Authentication Using Symmetric Encryption
- Mutual Authentication
- One-Way Authentication
3.2.1 Mutual Authentication
- [NEED78]
- [DENN81, DENN82]
- [KEHN92]
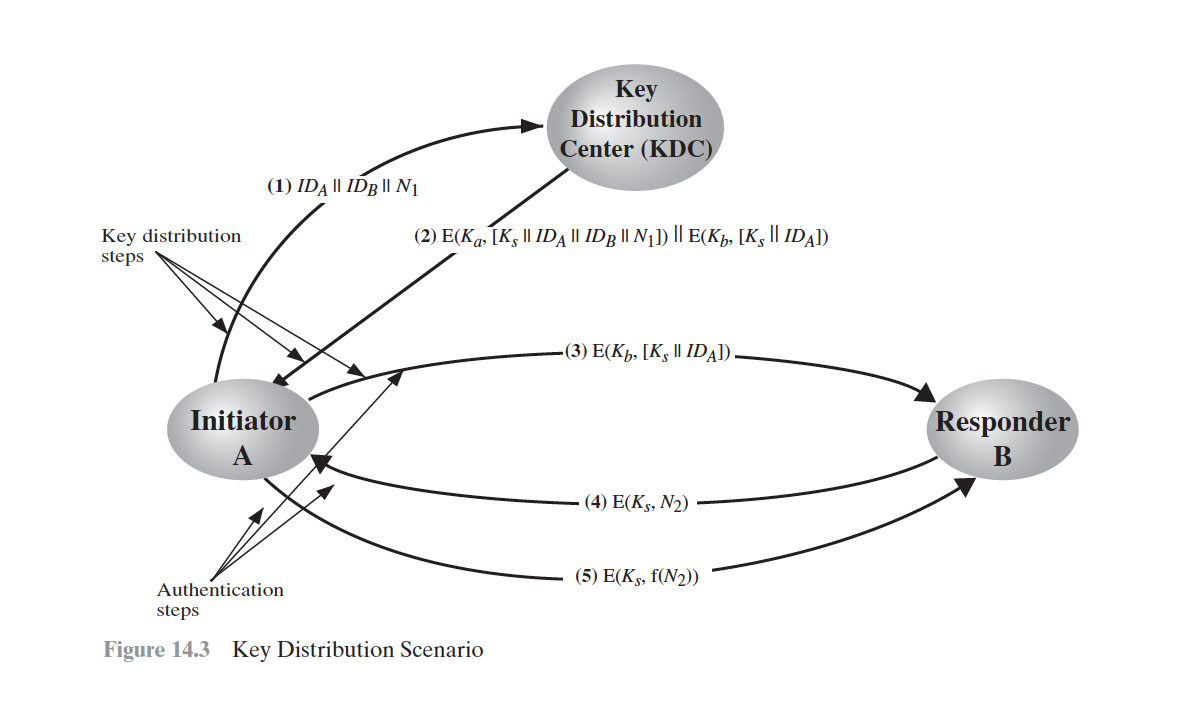
[NEED78]
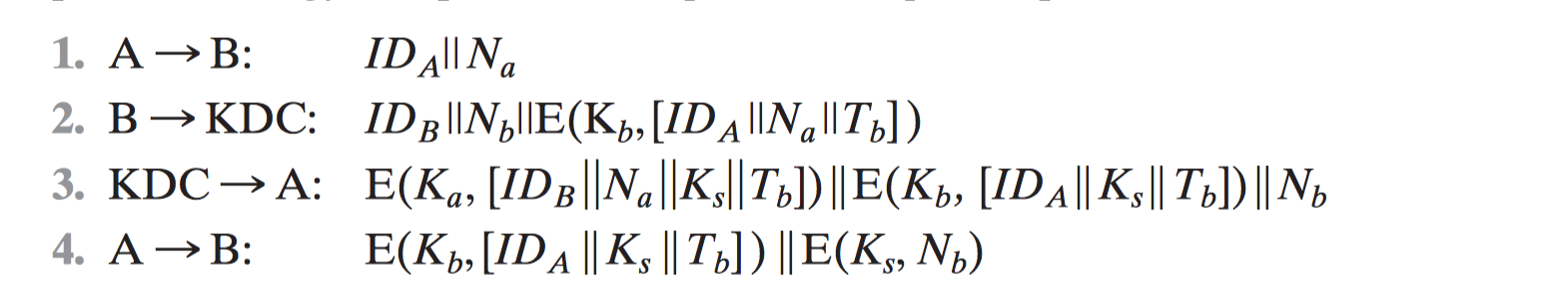
[DENN81, DENN82]
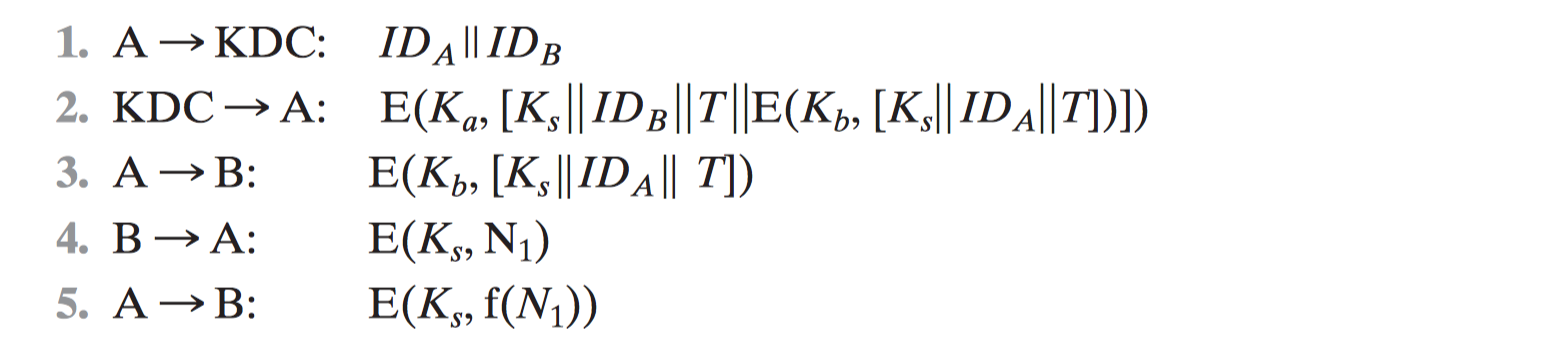
[KEHN92]
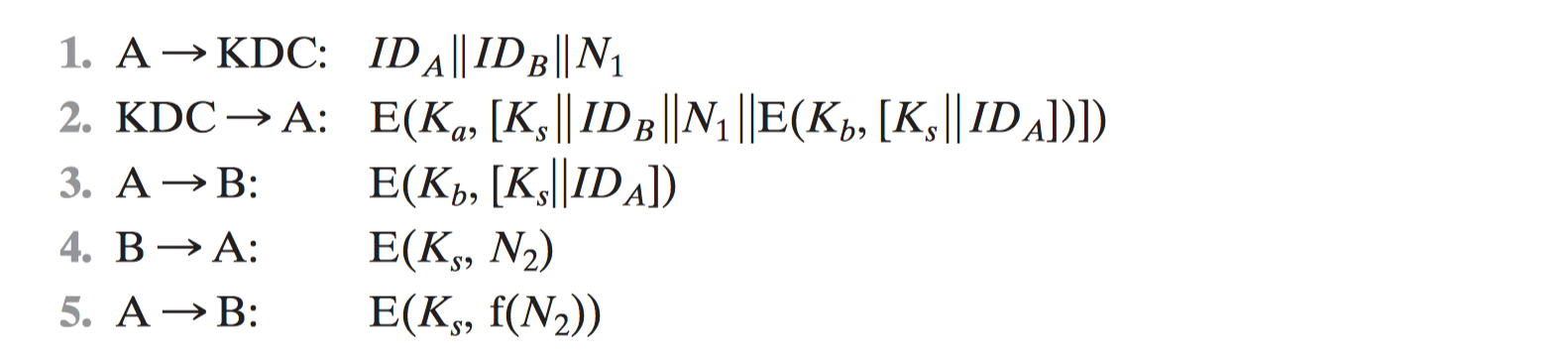
3.2.2 One-Way Authentication
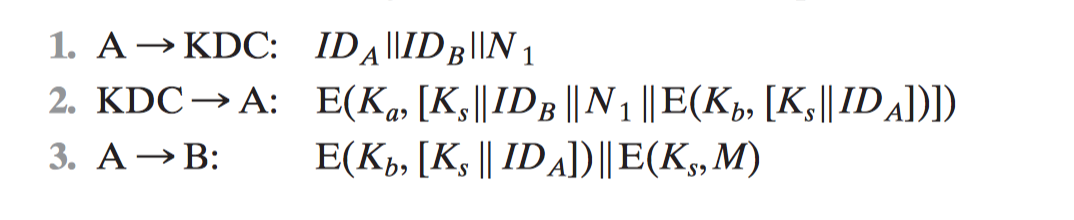
#3.3 Kerberos
Versions
Kerberos v4
Kerberos v5
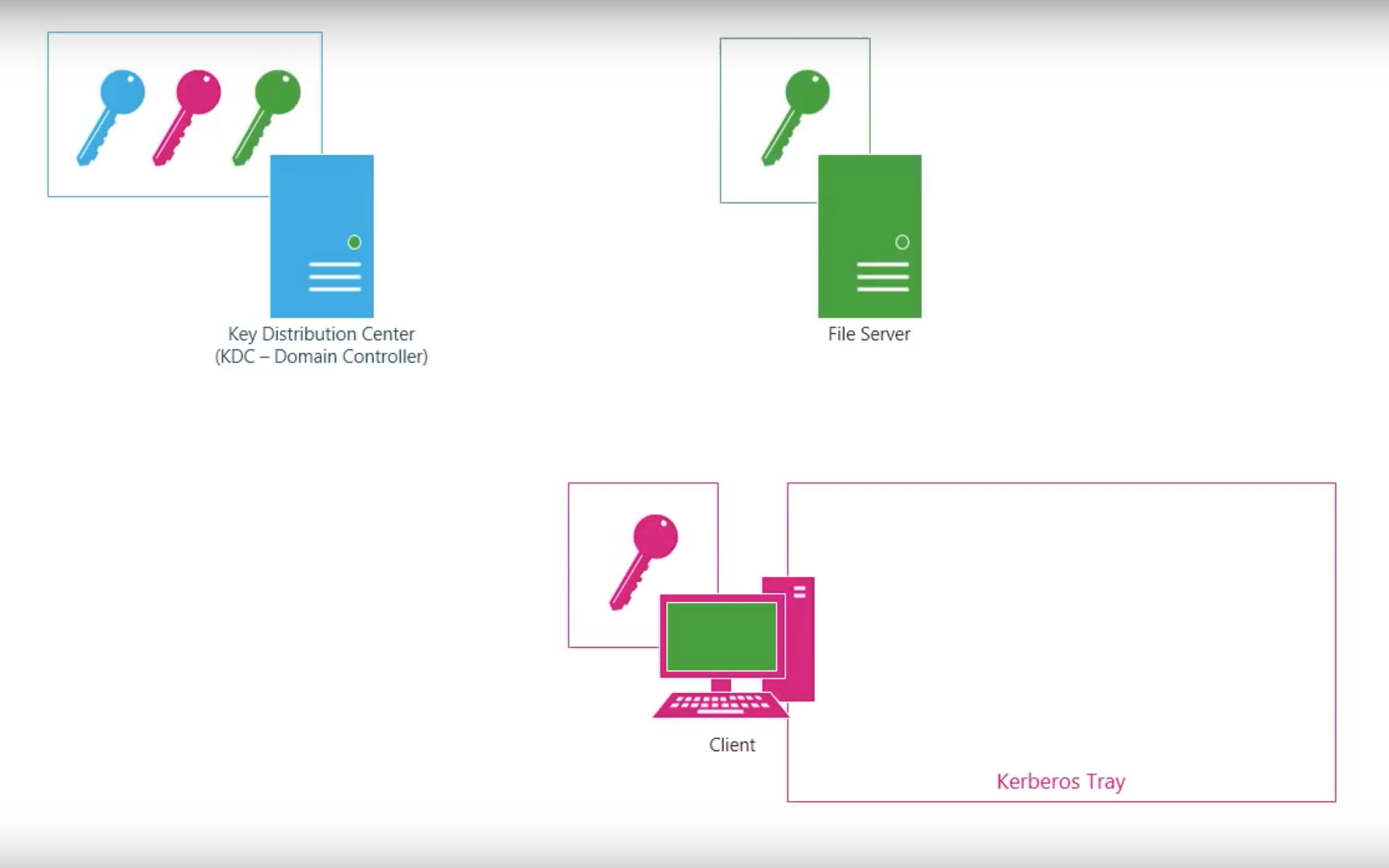
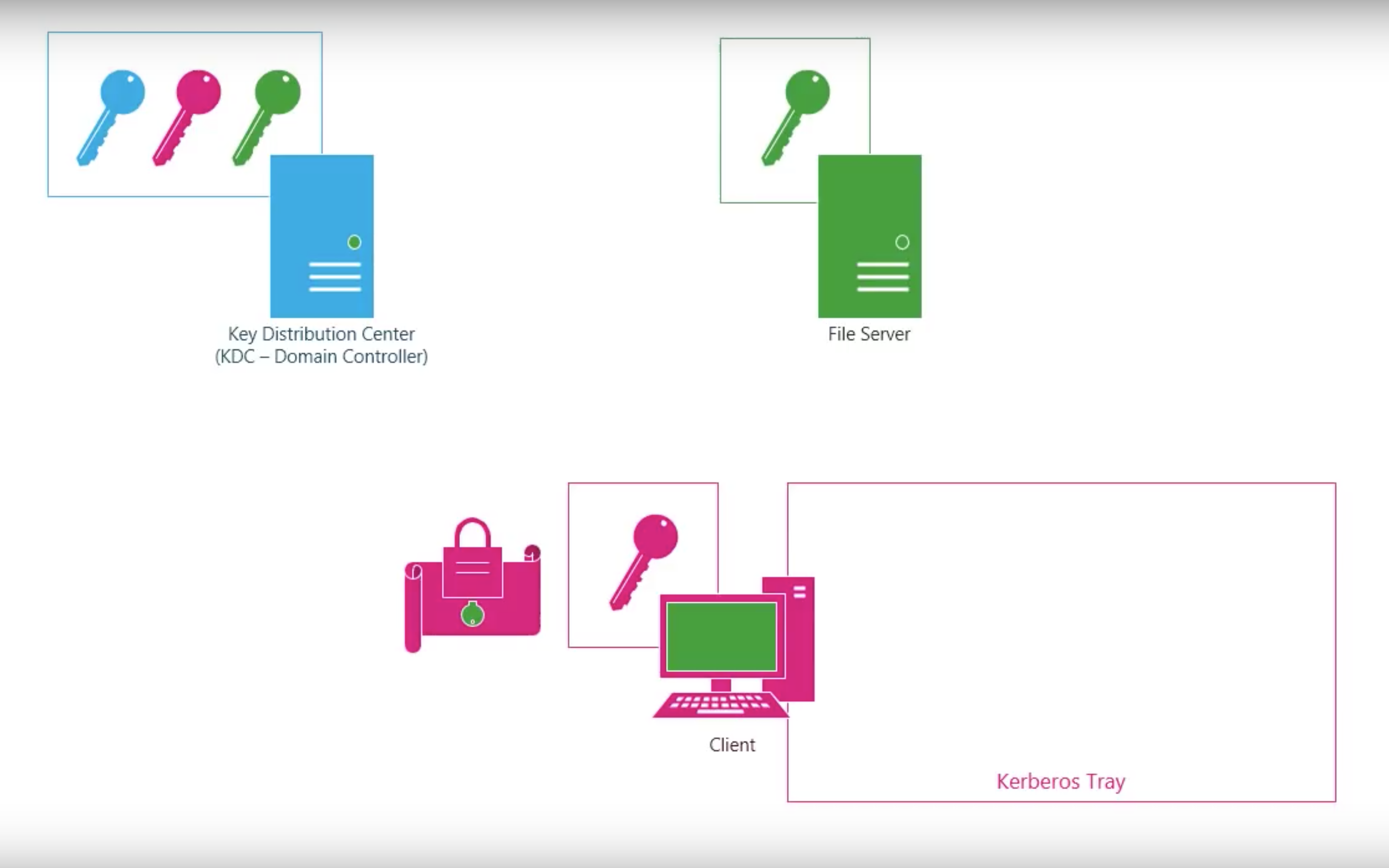
Kerberos V4
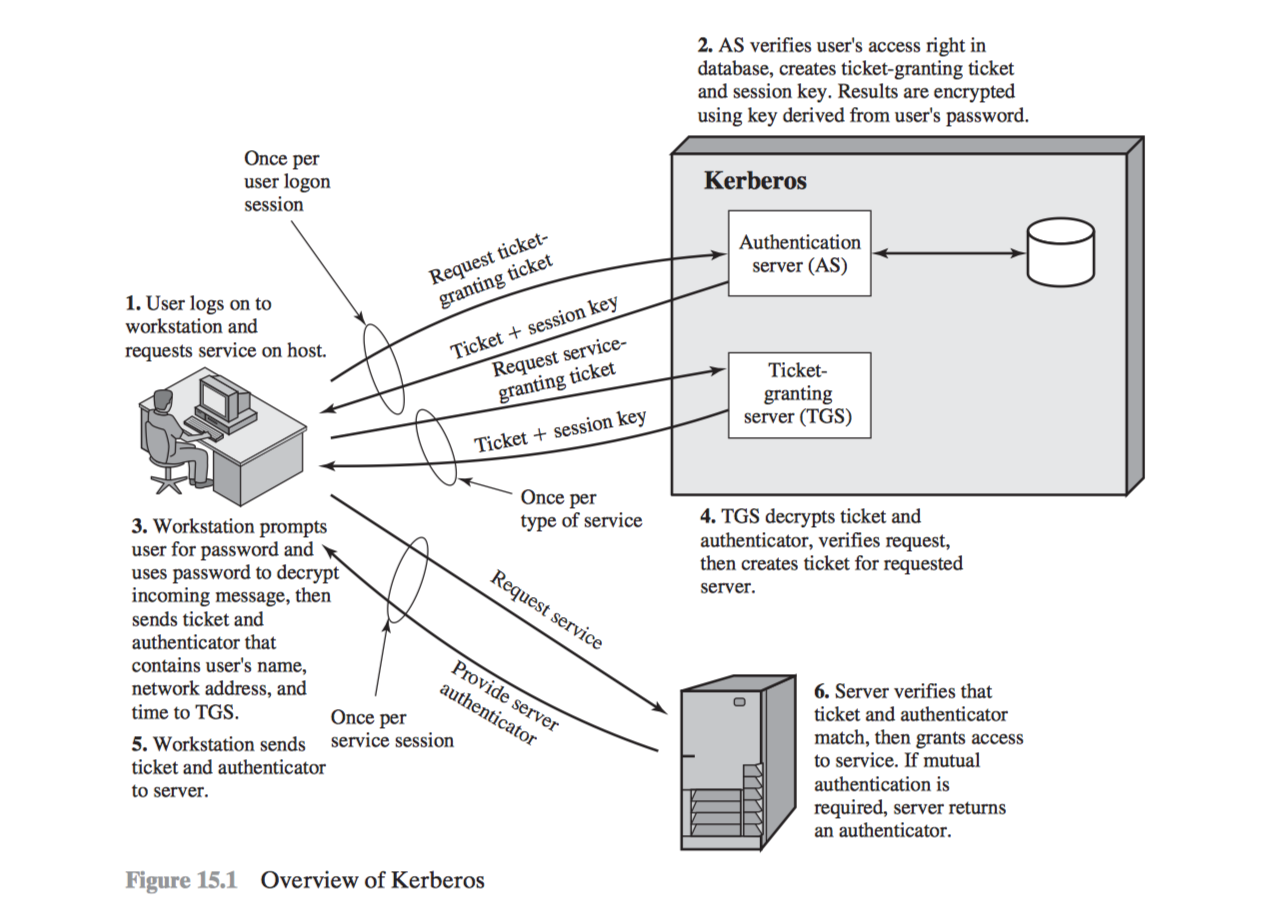
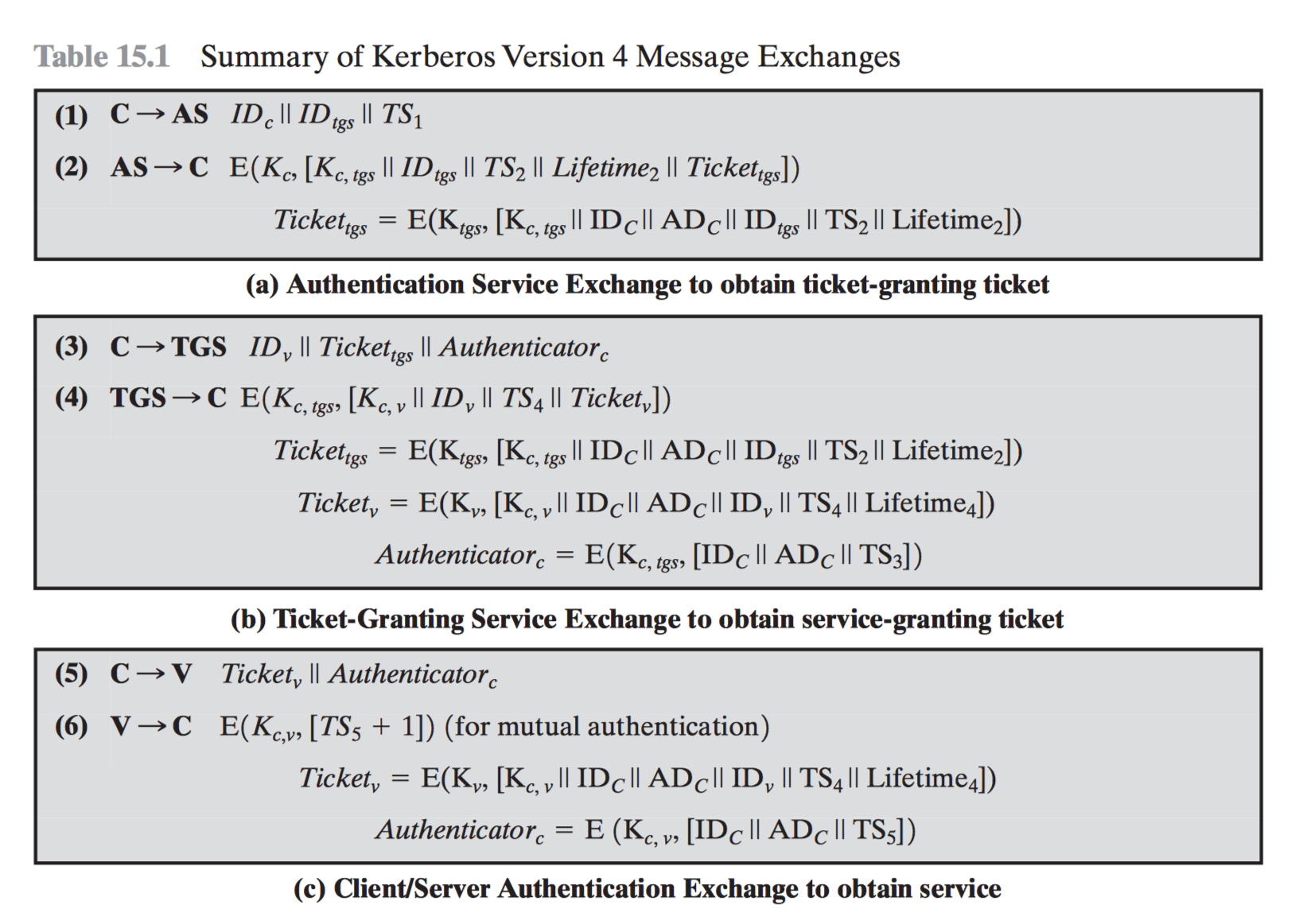
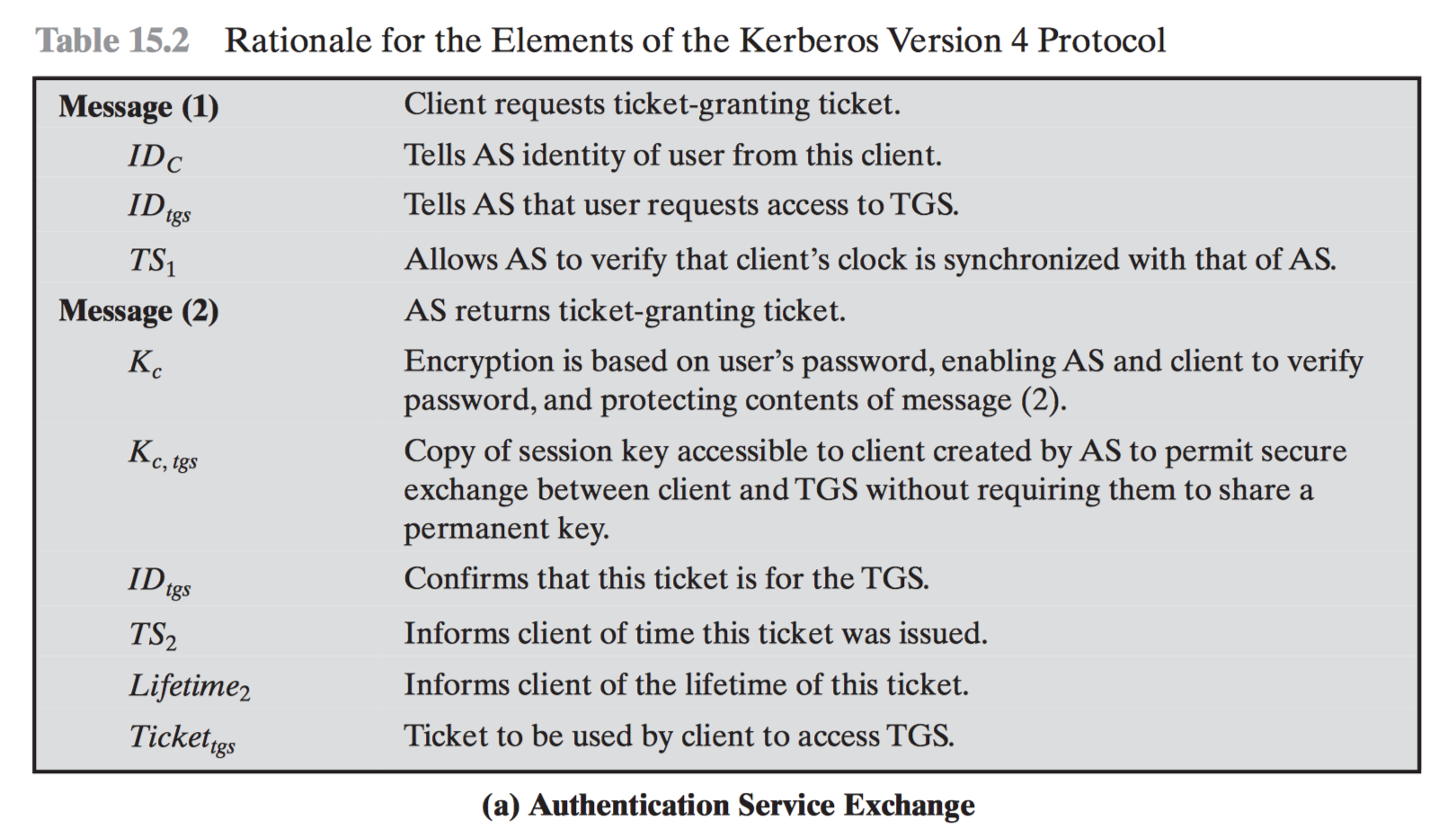
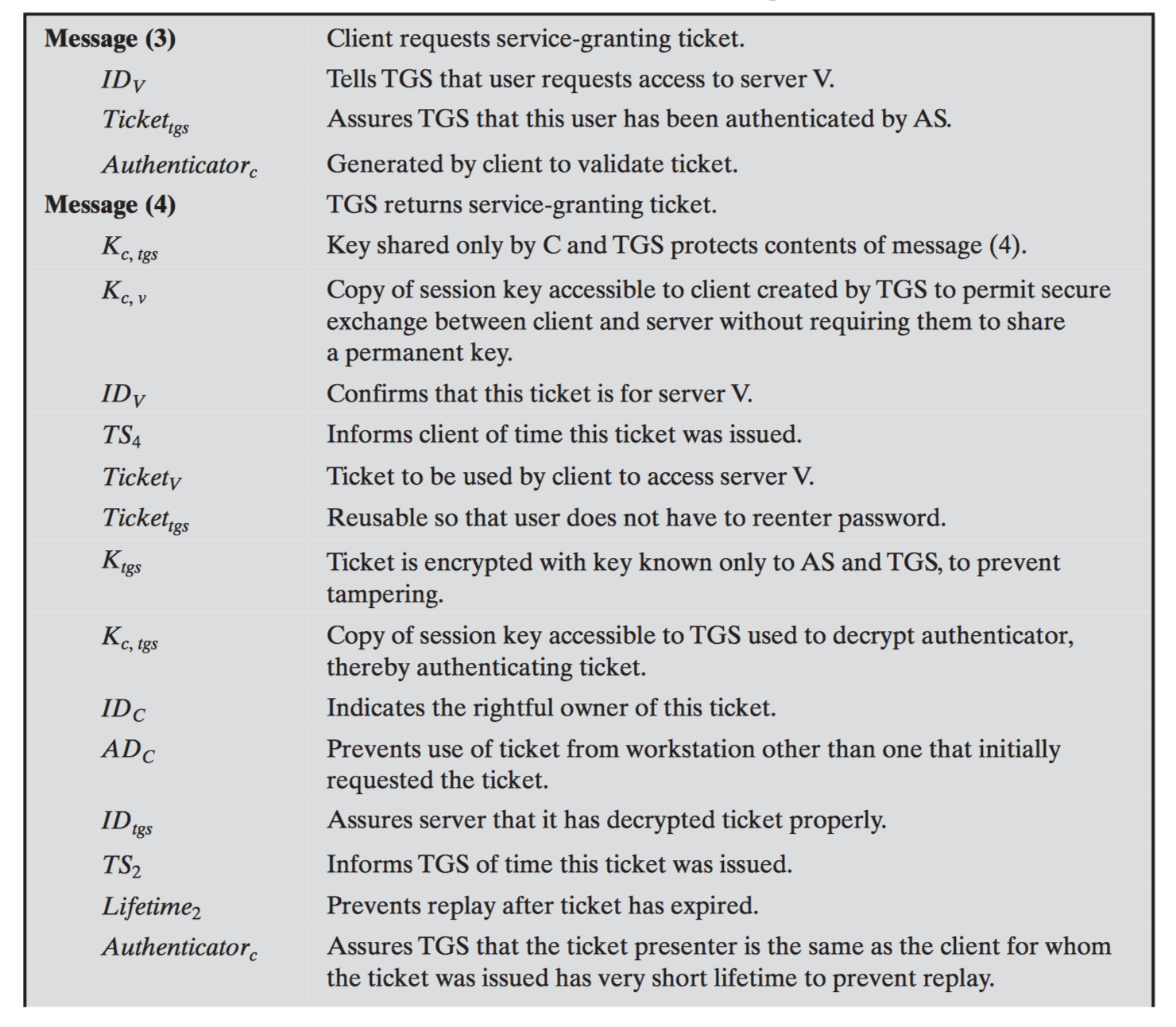

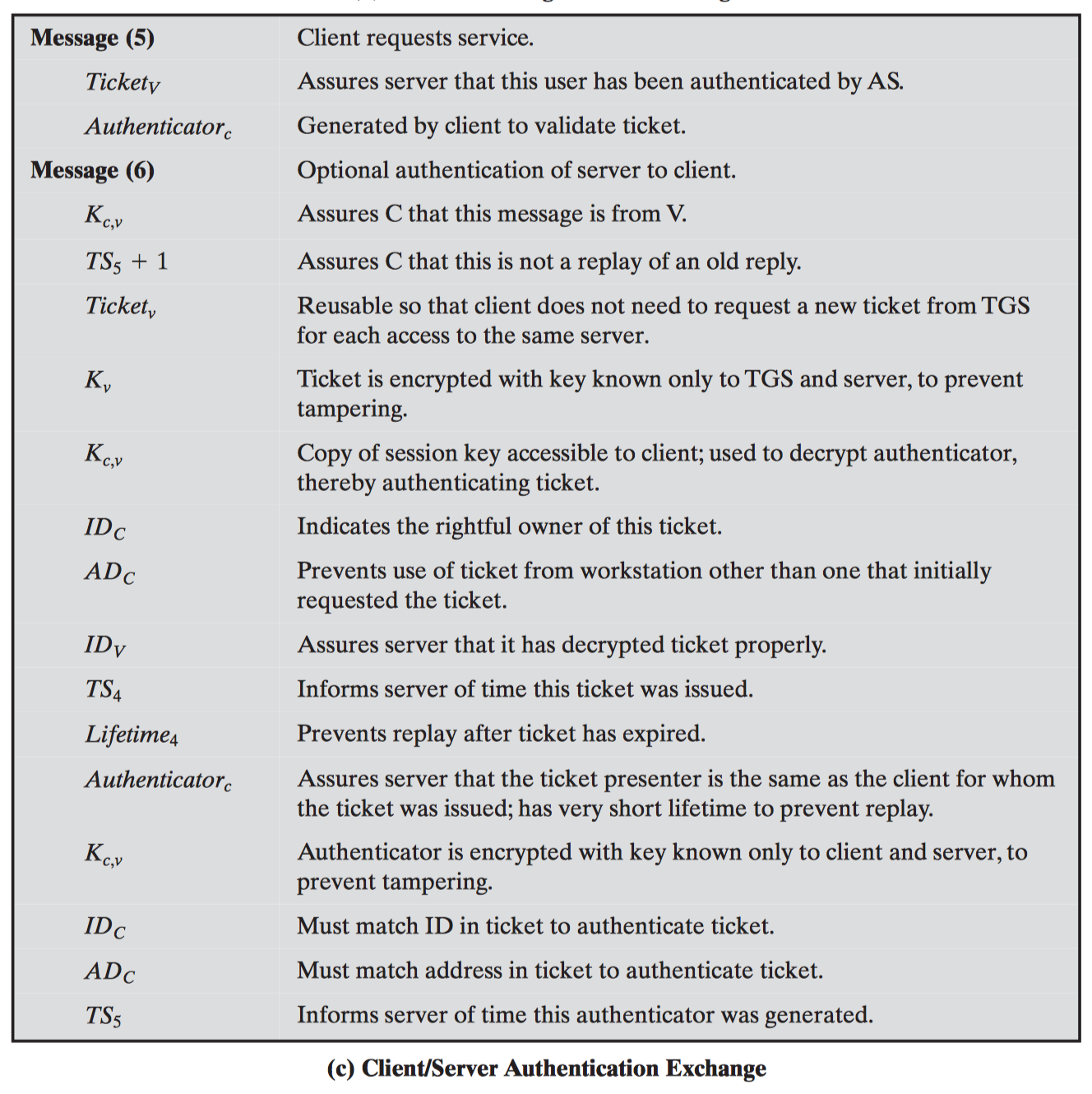
Step by step
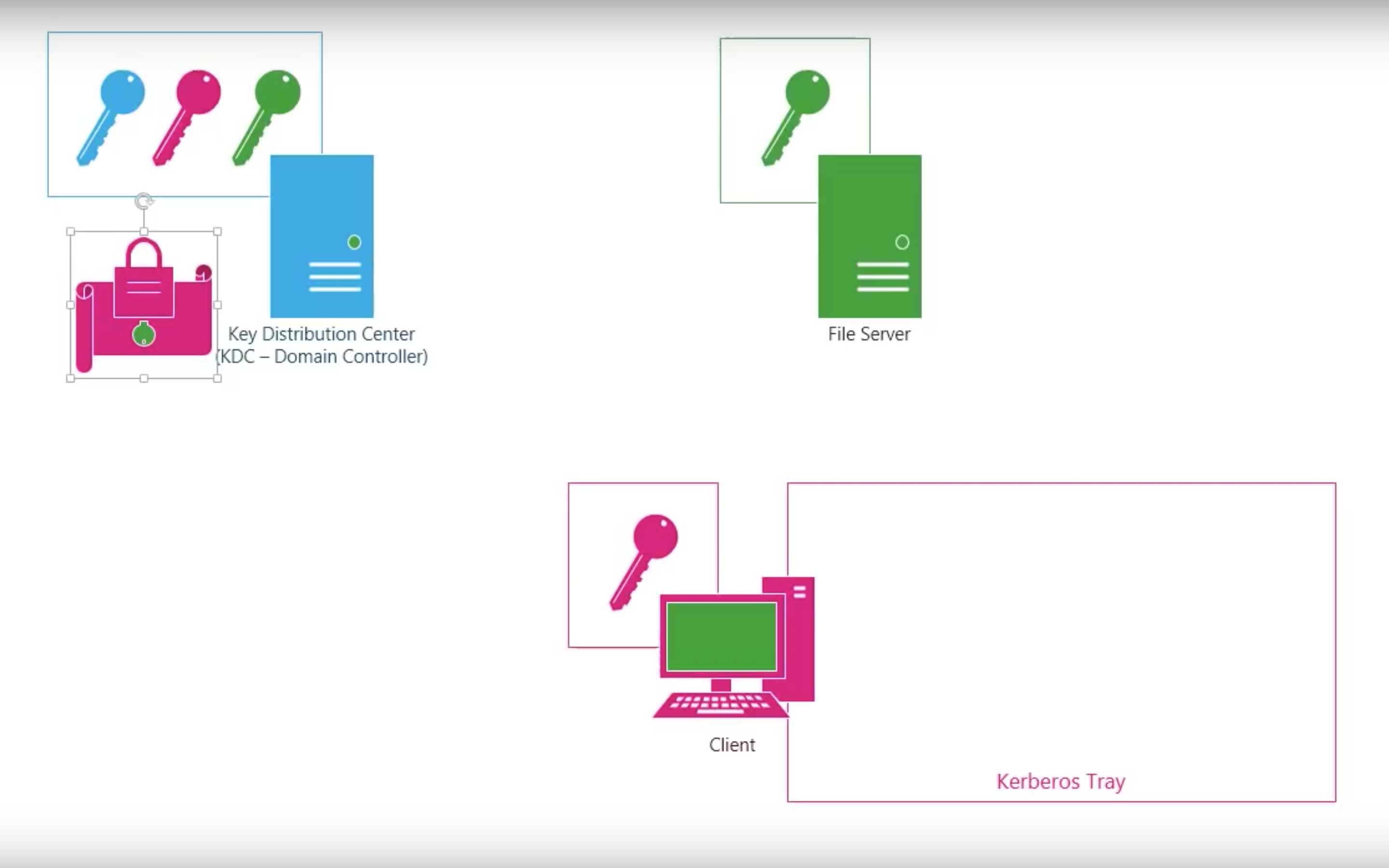
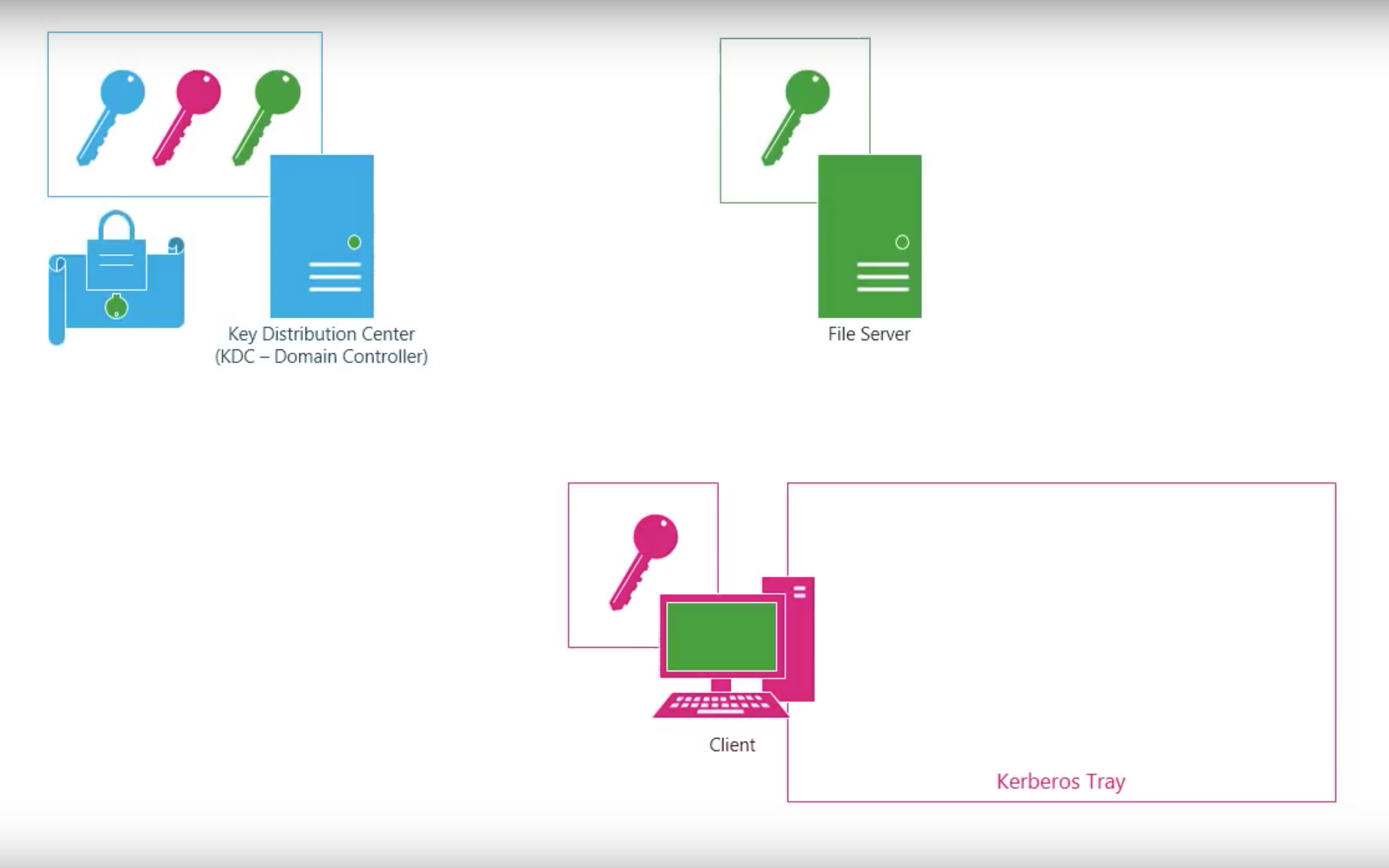
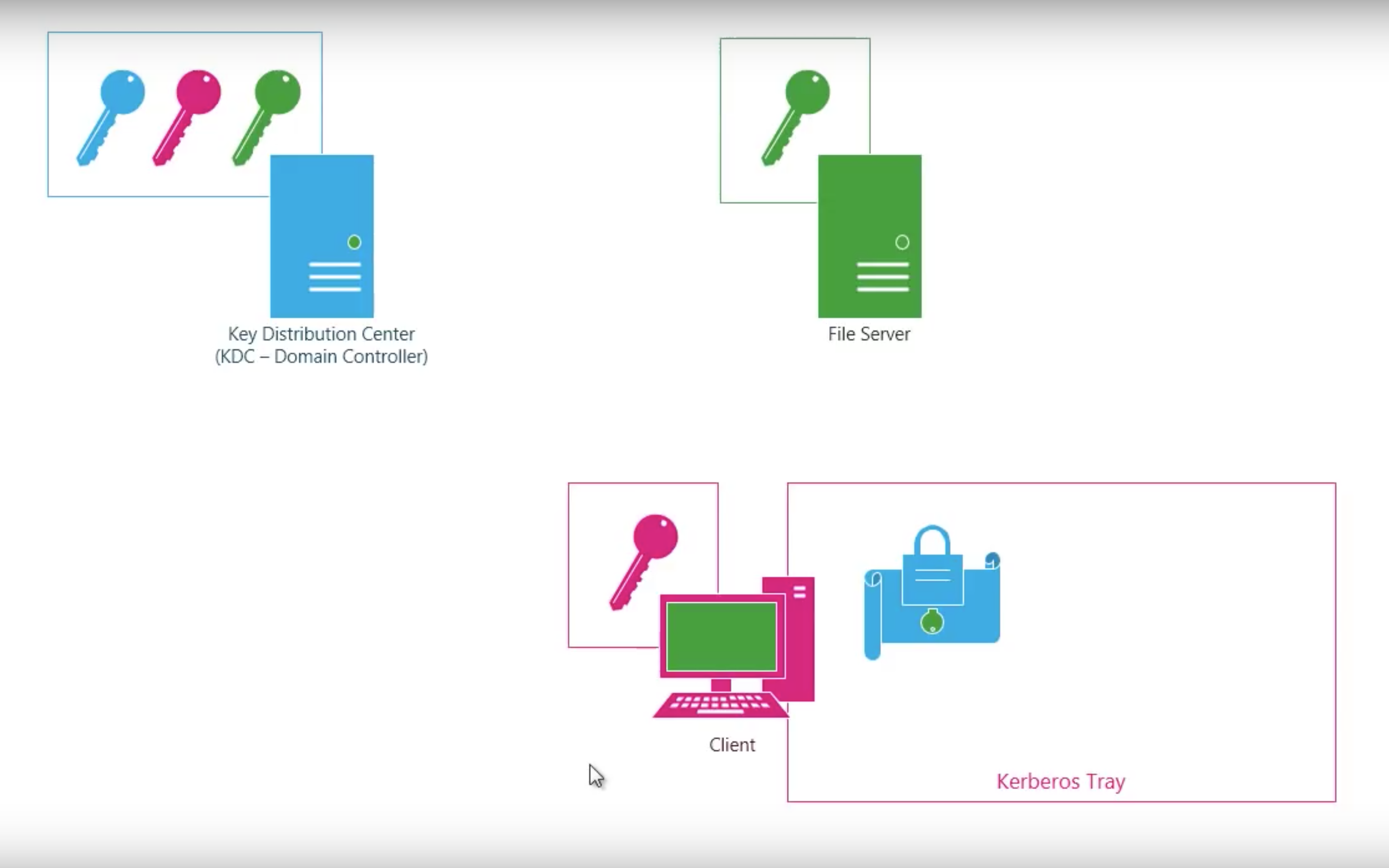
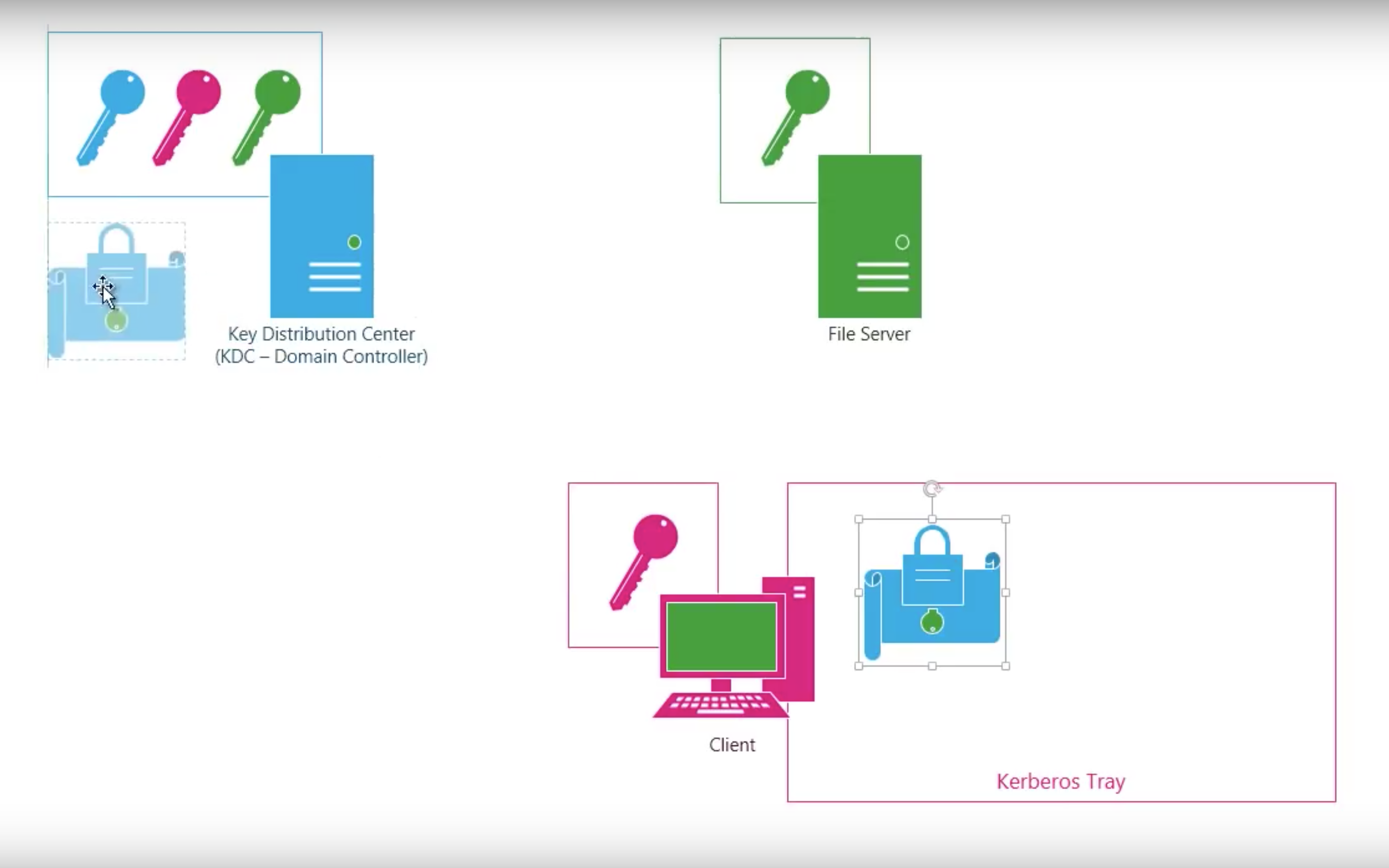
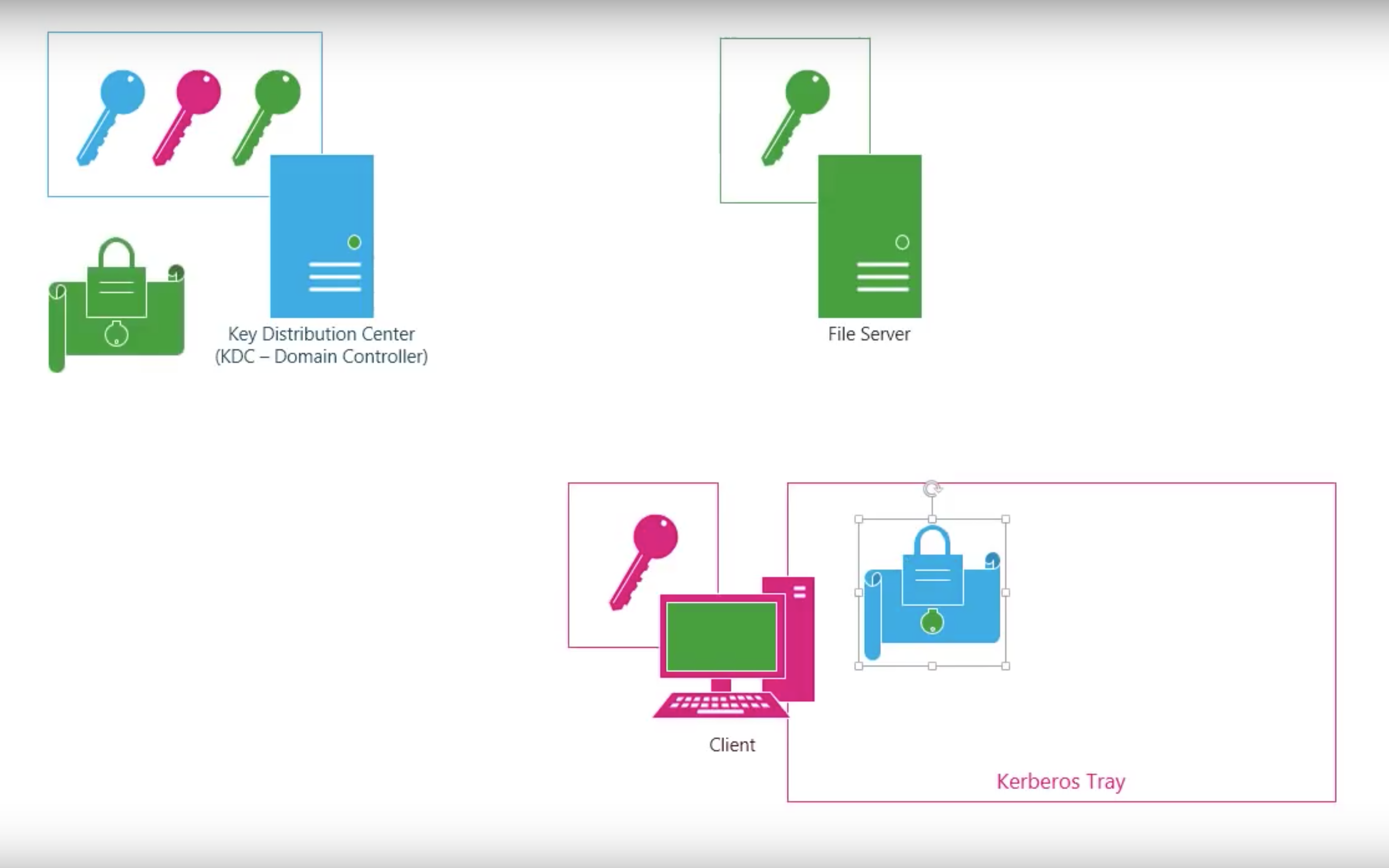
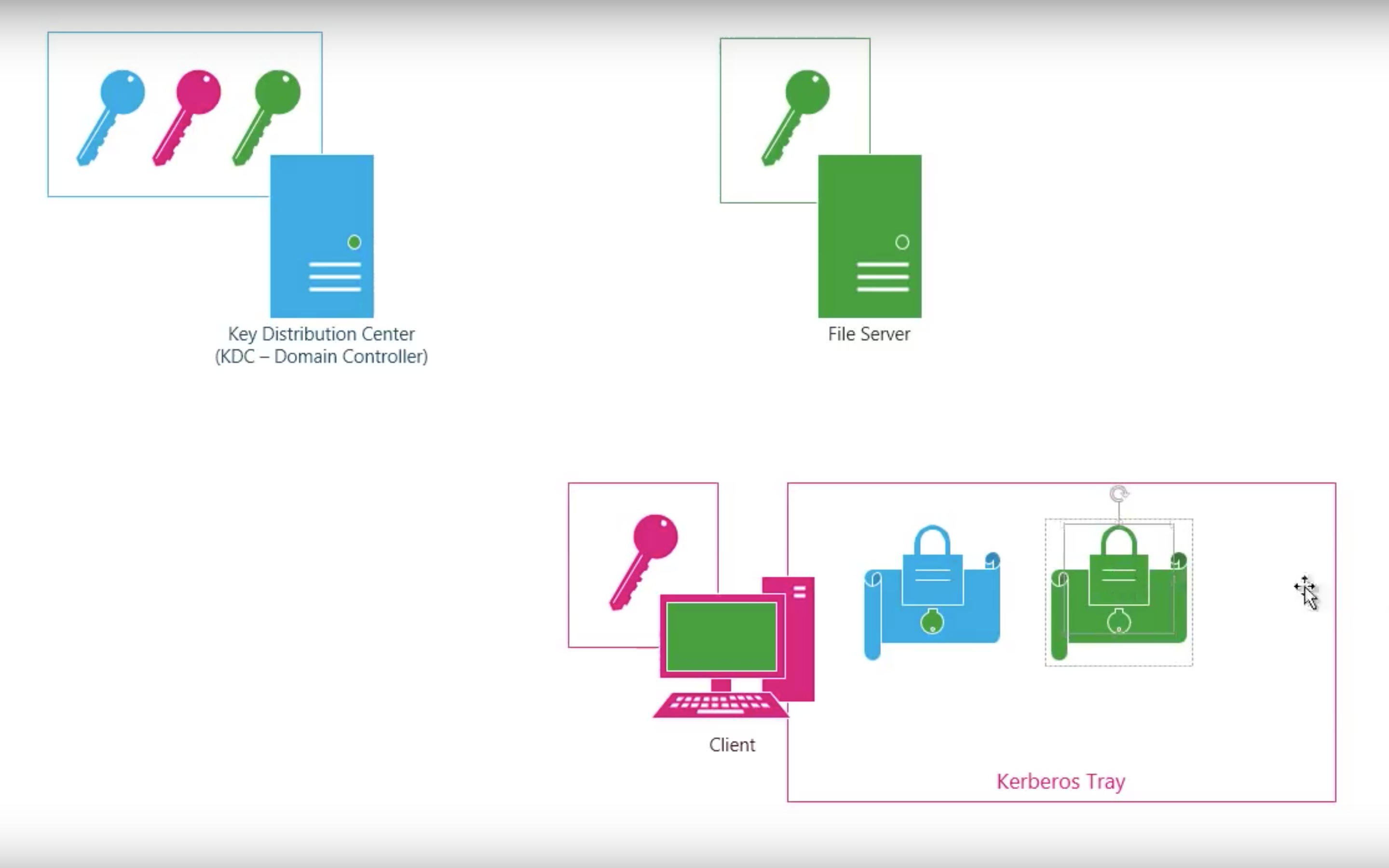
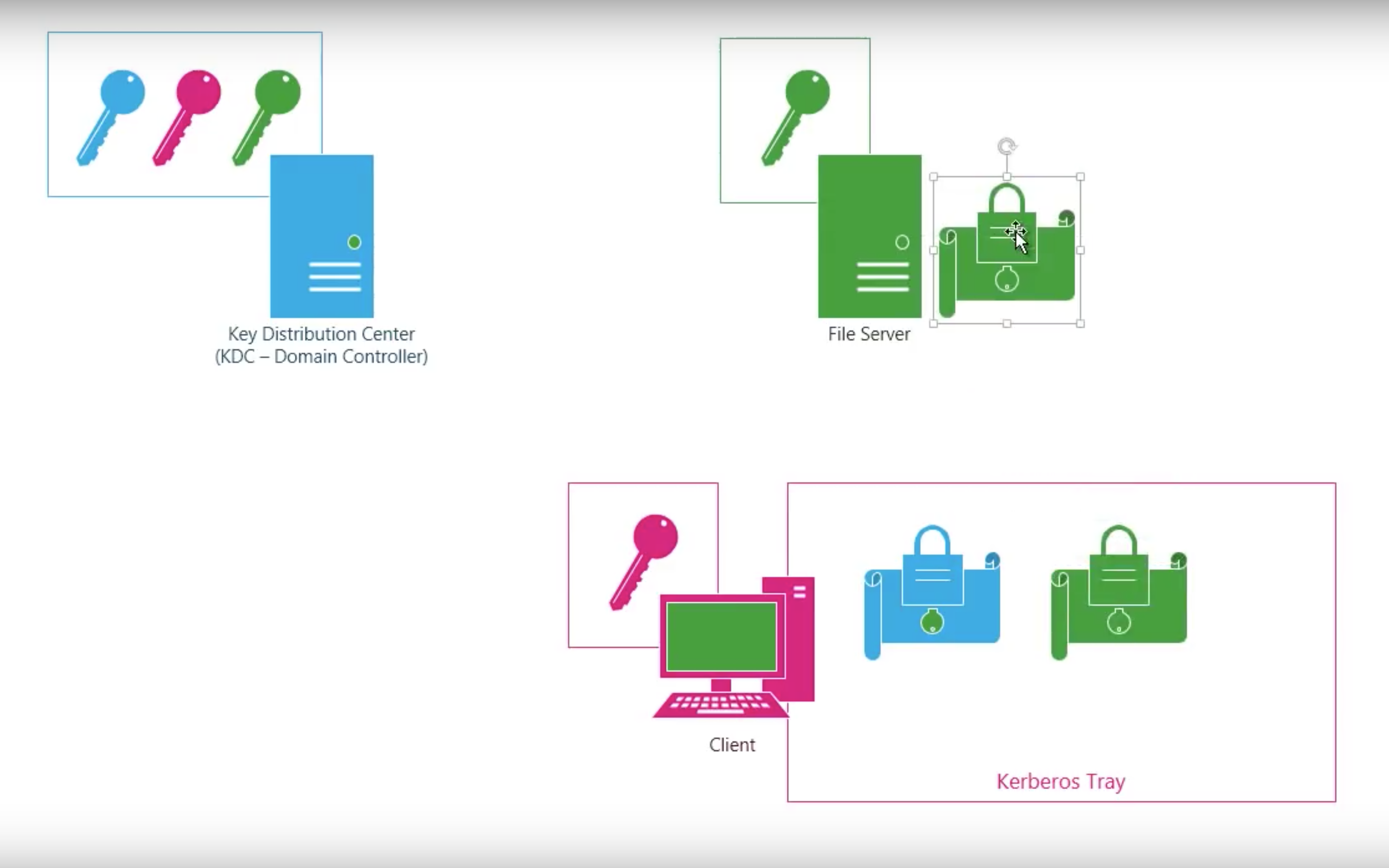
Shortcomings of Kerberos V4
- Environment Shortcomings
- Technical Deficiencies
Environment Shortcomings
- Encryption system dependence
- Internet protocol dependence
- Message Byte Ordering
- Ticket Lifetime
- Authentication Forwarding
- Inter-Realm Authentication
Encryption system dependence
- DES Dependency of v4
Internet protocol dependence
-IP Protocol Addresses only
Message Byte Ordering
- Did not follow convention of byte ordering/ was ambigious
- ASN.1 - Abstract Syntax Notation One
- BER - Basic Encoding Rules
Ticket Lifetime
- 8 bit life time
- Unit of 5 mins
- total (2^8)*5 = 1280 mins ~= 21 hours
- Explicit start and end time in v5
Authentication Forwarding
- No forwarding of credentials
- Example - Printing a File on a network
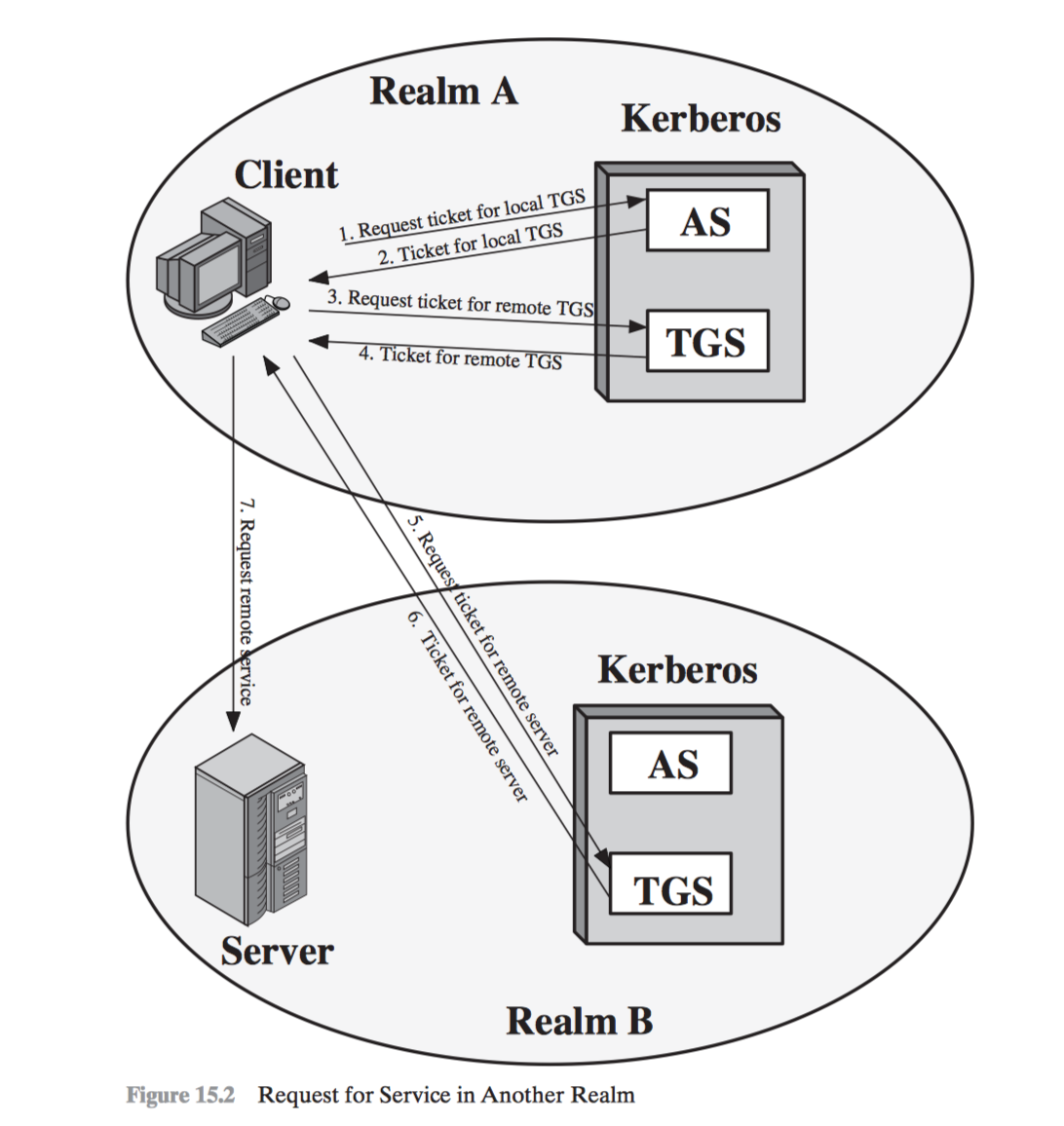
Inter-Realm Authentication
- Lack of interoperability
- N Realms = (N^2) Kerberos-to-kerberos relationships
Technical Deficiencies
- Double Encryption
- PCBC Encryption
- Session Key
- Password Attacks
Double Encryption
- Redundant Double encryption
- Removed in v5
PCBC Encryption mode in DES
- Propagating Cipher Block Chaining
- Non-standard
Session Key
- Possible threat of replay attack
- Use of sub-session key between client and server
Password Attacks
- Vulnerable to password attack
- Bruteforce or dictionary attacks
Kerberos V5

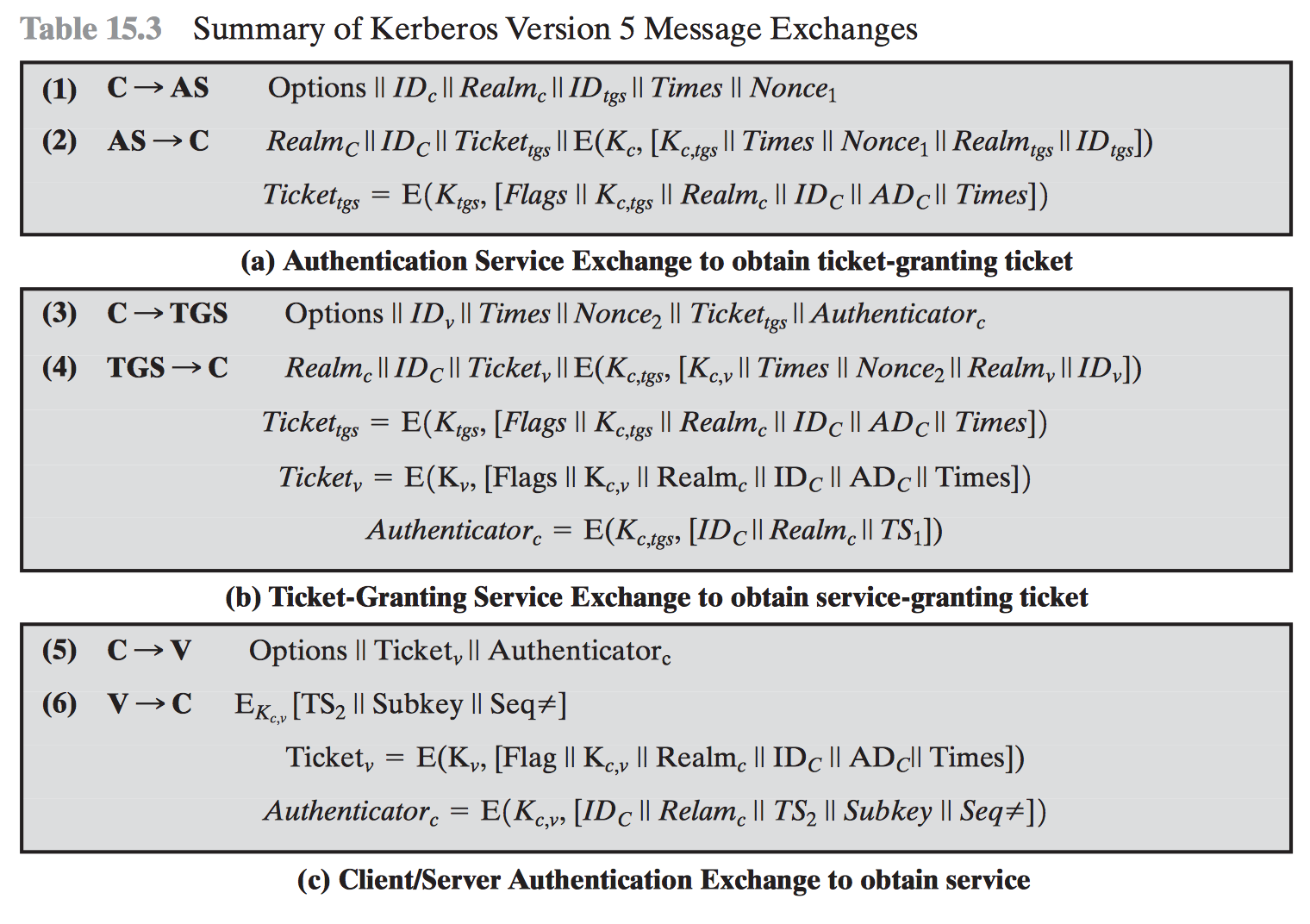
https://goo.gl/v7HTXh
Remote User Authentication Using Asymmetric Encryption
- Mutual Authentication
- One-Way Authentication

Asymmetric

Symmetric [KEHN92]
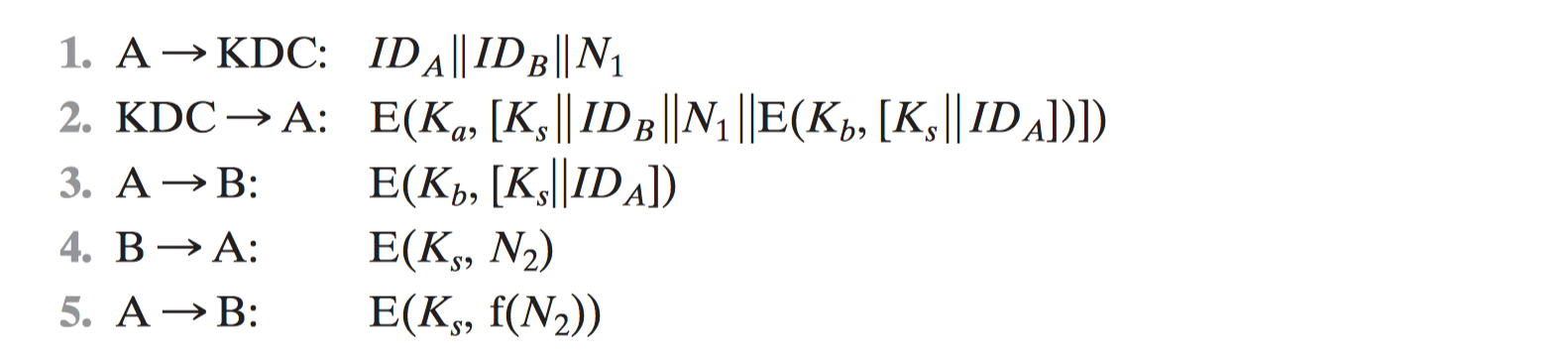
Federated Identity Management
- Identity Management
- Identity Federation
Federated identity management is a relatively new concept dealing with the use of a common identity management scheme across multiple enterprises and numerous applications and supporting many thousands, even millions, of users.
Identity Management
Identity management is a centralized, automated approach to provide enterprisewide access to resources by employees and other authorized individuals.
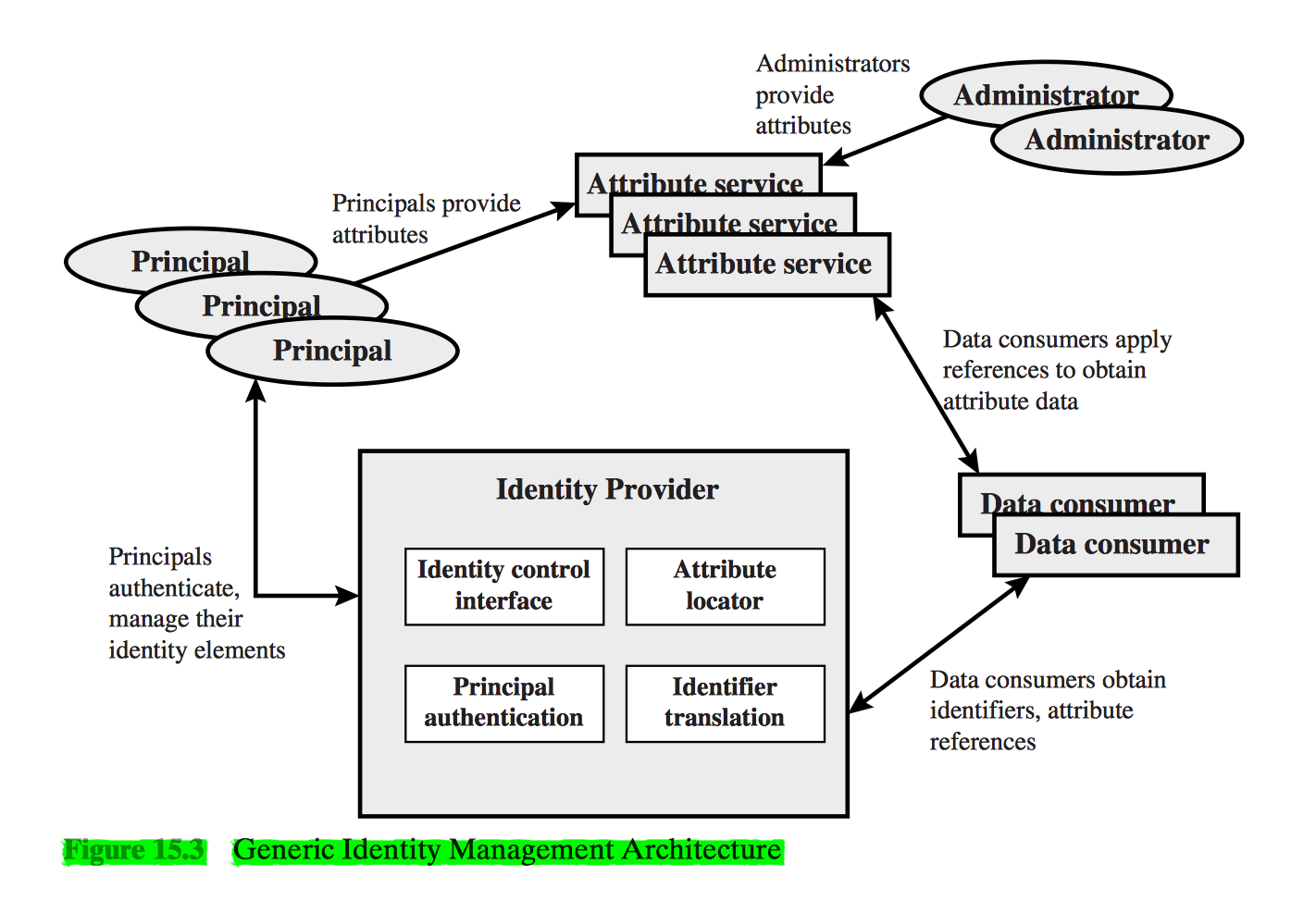
Principal Elements of Identity Management System
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Accounting
- Provisioning
- Workflow Automation
- Delegated Administration
- Password Synchronization
- Self-service Password Reset
- Federation
Identity Federation
Identity federation is, in essence, an extension of identity management to multiple security domains. Such domains include autonomous internal business units, external business partners, and other third-party applications and services.
The goal is to provide the sharing of digital identities so that a user can be authenticated a single time and then access applications and resources across multiple domains.